Gamma hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) for the treatment of alcohol dependence: a review
- PMID: 19578468
- PMCID: PMC2705225
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph6061917
Gamma hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) for the treatment of alcohol dependence: a review
Abstract
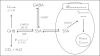
Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) is a short-chain fatty acid structurally similar to the inhibitory neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid. Clinical trials have demonstrated that 50-100 mg/kg of GHB fractioned into three or six daily doses is able to suppress alcohol withdrawal symptoms and facilitates the maintenance of abstinence from alcohol. These studies have also shown that GHB craving episodes are a very limited phenomenon (about 10-15%). Thus, physicians with access should consider the clinical efficacy of GHB as a valid pharmacological tool for the treatment of alcohol addiction.
Keywords: alcohol withdrawal syndrome; anti-craving drug; gamma-hydroxybutyric acid.
Figures

References
-
- Gianoulakis C. Implication of endogenous opioids and dopamine in alcoholism: human and basic science studies. Alcohol Alcoholism. 1996;31:33–42. - PubMed
-
- Bessmann SP, Fishbein WM. Gamma-hydroxybutyric, a normal brain metabolite. Nature. 1963;200:1207–1208. - PubMed
-
- Laborit H, Jouany JM, Gerard J, Fabiani F. Summary of an experimental and clinical study on a metabolic substrate with inhibitory central action: sodium 4-hydroxybutyrate. Presse Medicale. 1960;68:1867–1869. - PubMed
-
- Benavides J, Rumigny JF, Bourguignon JJ, Cash C, Wermuth CG, Mandel P, Vincendon G, Maitre M. High affinity binding sites for gamma-hydroxybutyric acid in rat brain. Life Sci. 1982;30:953–961. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

