Direct visualization of the lateral structure of porcine brain cerebrosides/POPC mixtures in presence and absence of cholesterol
- PMID: 19580752
- PMCID: PMC2711360
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2009.03.060
Direct visualization of the lateral structure of porcine brain cerebrosides/POPC mixtures in presence and absence of cholesterol
Abstract
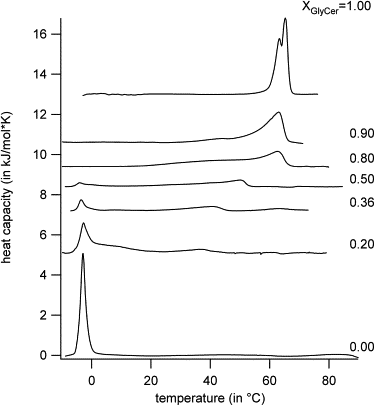
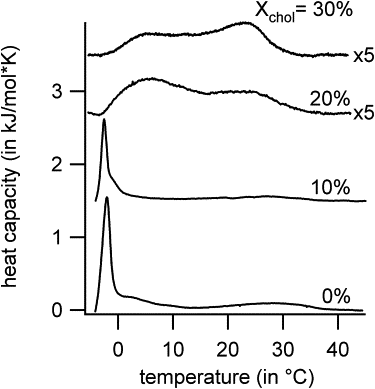
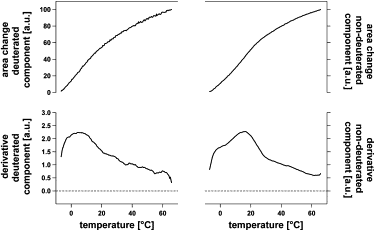
We studied the thermal behavior of membranes composed of mixtures of natural cerebrosides (from porcine brain) and 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (POPC) with and without cholesterol, using differential scanning calorimetry, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and confocal/multiphoton fluorescence microscopy. The POPC/cerebroside mixture display solid ordered/liquid disordered phase coexistence in a broad range of compositions and temperatures in agreement with previous results reported for POPC/(bovine brain)cerebrosides. The observed phase coexistence scenario consists of elongated, micrometer-sized cerebroside-rich solid ordered domains that span the bilayer, embedded in a POPC-rich liquid disordered phase. The data obtained from differential scanning calorimetry and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was in line with that obtained in the microscopy experiments for the binary mixture, except at very high cerebroside molar fractions (0.8-0.9) were some differences are observed. Cholesterol incorporation exerts strong changes on the lateral organization of POPC/porcine brain cerebroside membranes. At intermediate cholesterol concentrations (10-25 mol %) the solid ordered/liquid disordered phase coexistence scenario gradually transform to a solid ordered/liquid ordered one. Above 25 mol % of cholesterol two distinct regions with liquid ordered phase character are visualized in the membrane until a single liquid ordered phase forms at 40 mol % cholesterol. The observed cholesterol effect largely differs from that reported for POPC/porcine brain ceramide, reflecting the impact of the sphingolipids polar headgroup on the membrane lateral organization.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Absence of fluid-ordered/fluid-disordered phase coexistence in ceramide/POPC mixtures containing cholesterol.Biophys J. 2006 Jun 15;90(12):4437-51. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.077107. Epub 2006 Mar 24. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16565051 Free PMC article.
-
Lowering line tension with high cholesterol content induces a transition from macroscopic to nanoscopic phase domains in model biomembranes.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019 Feb 1;1861(2):478-485. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.11.010. Epub 2018 Dec 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2019. PMID: 30529459 Free PMC article.
-
Direct visualization of the lateral structure of giant vesicles composed of pseudo-binary mixtures of sulfatide, asialo-GM1 and GM1 with POPC.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018 Feb;1860(2):544-555. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2017.10.022. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2018. PMID: 29106974
-
Imaging cerebroside-rich domains for phase and shape characterization in binary and ternary mixtures.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Jul;1798(7):1357-67. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2009.11.013. Epub 2009 Nov 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19945421 Review.
-
Phase separation in lipid membranes.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Apr 1;3(4):a004630. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a004630. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 21441593 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Mixing brain cerebrosides with brain ceramides, cholesterol and phospholipids.Sci Rep. 2019 Sep 16;9(1):13326. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50020-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31527655 Free PMC article.
-
Cholesterol segregates into submicrometric domains at the living erythrocyte membrane: evidence and regulation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Dec;72(23):4633-51. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1951-x. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 26077601 Free PMC article.
-
Micrometric segregation of fluorescent membrane lipids: relevance for endogenous lipids and biogenesis in erythrocytes.J Lipid Res. 2013 Apr;54(4):1066-76. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M034314. Epub 2013 Jan 14. J Lipid Res. 2013. PMID: 23322884 Free PMC article.
-
Recent progress on lipid lateral heterogeneity in plasma membranes: From rafts to submicrometric domains.Prog Lipid Res. 2016 Apr;62:1-24. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2015.12.004. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Prog Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 26738447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigating lipids as a source of chemical exchange-induced MRI frequency shifts.NMR Biomed. 2017 Apr;30(4):10.1002/nbm.3525. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3525. Epub 2016 Apr 13. NMR Biomed. 2017. PMID: 27076394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen Y.Q., Rafi M.A., de Gala G., Wenger D.A. Cloning and expression of cDNA encoding human galactocerebrosidase, the enzyme deficient in globoid cell leukodystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1993;2:1841–1845. - PubMed
-
- Hansson G.C. The subcellular localization of the glycosphingolipids in the epithelial cells of rat small intestine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1983;733:295–299. - PubMed
-
- Hauser H., Howell K., Dawson R.M., Bowyer D.E. Rabbit small intestinal brush border membrane preparation and lipid composition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1980;602:567–577. - PubMed
-
- Norton W.T., Abe T., Poduslo S.E., DeVries G.H. The lipid composition of isolated brain cells and axons. J. Neurosci. Res. 1975;1:57–75. - PubMed
-
- Tan R.X., Chen J.H. The cerebrosides. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2003;20:509–534. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

