The effect of concurrent androgen deprivation and 3D conformal radiotherapy on prostate volume and clinical organ doses during treatment for prostate cancer
- PMID: 19581310
- PMCID: PMC3473383
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr/65939531
The effect of concurrent androgen deprivation and 3D conformal radiotherapy on prostate volume and clinical organ doses during treatment for prostate cancer
Abstract
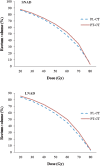
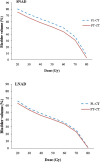
In this study, we investigated the shrinking effect of concurrent three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy (3D-CRT) and androgen deprivation (AD) on prostate volume, and its possible impact on the dose received by the rectum and bladder during the course of 3D-CRT. The difference between the prostatic volumes determined on pre-treatment planning CT (PL-CT) and post-treatment CT (PT-CT) following a 3D-CRT course was assessed in 52 patients with localised prostate carcinoma. The changes in mean prostate volume when compared with PL-CT and PT-CT-based measurements were assessed. The pre- and post-treatment mean prostate volumes for the whole study population were 49.7 cm(3) and 41.0 cm(3) (p _ 0.02), respectively. The study cohort was divided into two groups depending on the duration of neoadjuvant androgen deprivation (NAD): 23 patients (44.7%) were designated as "short NAD" (< or =3 months; SNAD) and the remaining 29 (55.3%) as "long NAD" (>3 months; LNAD). Patients on SNAD experienced a significantly greater reduction in prostate volume compared with those on LNAD (14.1% vs 5.1%; p _ 0.03). A significant increase in rectum V(40-60) values in PT-CT compared with PL-CT was demonstrated. LNAD patients had significantly higher rectal V(50-70) values at PT-CT compared with the SNAD group. There was a significant decline in V(30)-V(75) bladder values in PT-CT compared with PL-CT in the SNAD group. In conclusion, a higher prostate volume reduction during 3D-CRT was demonstrated when RT planning was performed within 3 months of NAD. However, this reduction and daily organ motion may lead to an unpredictable increase in rectal doses.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-dose radiotherapy with short-term or long-term androgen deprivation in localised prostate cancer (DART01/05 GICOR): a randomised, controlled, phase 3 trial.Lancet Oncol. 2015 Mar;16(3):320-7. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(15)70045-8. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Lancet Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25702876 Clinical Trial.
-
Neoadjuvant androgen deprivation and prostate gland shrinkage during conformal radiotherapy.Radiother Oncol. 2003 Feb;66(2):151-7. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(03)00031-8. Radiother Oncol. 2003. PMID: 12648786
-
High-dose radiotherapy plus prolonged hormone therapy in CT2-3 prostatic carcinoma: is it useful?Tumori. 2004 Mar-Apr;90(2):201-7. doi: 10.1177/030089160409000208. Tumori. 2004. PMID: 15237583 Clinical Trial.
-
Rotational 3D-conformal radiation therapy (conformation therapy) combined with hormone therapy for the treatment of stage B2/C prostate cancer in Japanese men.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003 May 1;56(1):208-12. doi: 10.1016/s0360-3016(03)00084-1. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003. PMID: 12694840 Review.
-
Technological advances in radiotherapy for the treatment of localised prostate cancer.Eur J Cancer. 2005 Apr;41(6):908-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2004.12.028. Eur J Cancer. 2005. PMID: 15808957 Review.
Cited by
-
MRI-Guided Radiation Therapy for Prostate Cancer: The Next Frontier in Ultrahypofractionation.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 21;15(18):4657. doi: 10.3390/cancers15184657. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous integrated boost to intraprostatic lesions using different energy levels of intensity-modulated radiotherapy and volumetric-arc therapy.Br J Radiol. 2014 Feb;87(1034):20130617. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20130617. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Br J Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24319009 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of androgen deprivation therapy on setup errors during external beam radiation therapy for prostate cancer.Strahlenther Onkol. 2017 Jun;193(6):472-482. doi: 10.1007/s00066-017-1131-z. Epub 2017 Apr 13. Strahlenther Onkol. 2017. PMID: 28409246 English.
-
Relationship between prostate volume changes and treatment duration of neoadjuvant androgen deprivation during intensity-modulated radiation therapy for Japanese patients with prostate cancer.Nagoya J Med Sci. 2016 Aug;78(3):313-21. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27578915 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of androgen deprivation therapy on 68Ga-PSMA tracer uptake in non-metastatic prostate cancer patients.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020 Mar;47(3):632-641. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04581-4. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31732768
References
-
- Bolla M, Gonzalez D, Warde P, Dubois JB, Mirimanoff RO, Storme G, et al. Improved survival in patients with locally advanced prostate cancer treated with radiotherapy and goserelin. N Engl J Med 1997;337:295–300 - PubMed
-
- Pilepich MV, Caplan R, Byhardt RW, Lawton CA, Gallagher MJ, Mesic JB, et al. Phase III trial of androgen suppression using goserelin in unfavorable-prognosis carcinoma of the prostate treated with definitive radiotherapy: report of Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Protocol 85-31. J Clin Oncol 1997;15:1013–21 - PubMed
-
- Bolla M, Collette L, Blank L, Warde P, Dubois JB, Mirimanoff RO, et al. Long-term results with immediate androgen suppression and external irradiation in patients with locally advanced prostate cancer (an EORTC study): a phase III randomised trial. Lancet 2002;360:103–6 - PubMed
-
- Roach M, 3rd, DeSilvio M, Lawton C, Uhl V, Machtay M, Seider MJ, et al. Phase III trial comparing whole-pelvic versus prostate-only radiotherapy and neoadjuvant versus adjuvant combined androgen suppression: Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 9413. J Clin Oncol 2003;21:1904–11 - PubMed
-
- Pilepich MV, Winter K, John MJ, Mesic JB, Sause W, Rubin P, et al. Phase III radiation therapy oncology group (RTOG) trial 86–10 of androgen deprivation adjuvant to definitive radiotherapy in locally advanced carcinoma of the prostate. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2001;50:1243–52 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

