Role of porins in the susceptibility of Mycobacterium smegmatis and Mycobacterium chelonae to aldehyde-based disinfectants and drugs
- PMID: 19581465
- PMCID: PMC2737867
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00590-09
Role of porins in the susceptibility of Mycobacterium smegmatis and Mycobacterium chelonae to aldehyde-based disinfectants and drugs
Abstract
Nosocomial outbreaks attributable to glutaraldehyde-resistant, rapidly growing mycobacteria are increasing. Here, evidence is provided that defects in porin expression dramatically increase the resistance of Mycobacterium smegmatis and Mycobacterium chelonae to glutaraldehyde and another aldehyde disinfectant, ortho-phthalaldehyde. Since defects in porin activity also dramatically increased the resistance of M. chelonae to drugs, there is thus some concern that the widespread use of glutaraldehyde and ortho-phthalaldehyde in clinical settings may select for drug-resistant bacteria.
Figures
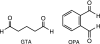


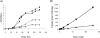
References
-
- Achouak, W., T. Heulin, and J.-M. Pagès. 2001. Multiple facets of bacterial porins. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 199:1-7. - PubMed
-
- Brennan, P. J., and H. Nikaido. 1995. The envelope of mycobacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 64:29-63. - PubMed
-
- Chroneou, A., S. K. Zimmerman, S. Cook, S. Willey, J. Eyre-Kelly, N. Zias, D. S. Shapiro, J. F. Beamis, and D. E. Craven. 2008. Molecular typing of Mycobacterium chelonae isolates from a pseudo-outbreak involving an automated bronchoscope washer. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 29:1088-1090. - PubMed
-
- Daffé, M., and P. Draper. 1998. The envelope layers of mycobacteria with reference to their pathogenicity. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 39:131-203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

