Late effects of conformal radiation therapy for pediatric patients with low-grade glioma: prospective evaluation of cognitive, endocrine, and hearing deficits
- PMID: 19581535
- PMCID: PMC2799064
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.21.2738
Late effects of conformal radiation therapy for pediatric patients with low-grade glioma: prospective evaluation of cognitive, endocrine, and hearing deficits
Abstract
Purpose: We conducted a prospective trial to evaluate late effects in pediatric patients with low-grade glioma (LGG) treated with conformal radiation therapy (CRT).
Patients and methods: Between August 1997 and August 2006, 78 pediatric patients with LGG (mean age, 9.7 years; standard deviation, +/-4.4 years) received 54 Gy of CRT with a 10-mm clinical target volume margin. Tumor locations were diencephalon (n = 58), cerebral hemisphere (n = 3), and cerebellum (n = 17). Baseline and serial evaluations were performed to identify deficits in cognition, endocrine function, and hearing. Deficits were correlated with clinical factors and radiation dose within specific normal tissue volumes.
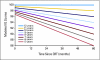
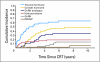
Results: Cognitive effects of CRT through 5 years after CRT correlated with patient age, neurofibromatosis type 1 status, tumor location and volume, extent of resection, and radiation dose. The effect of age exceeded that of radiation dose; patients younger than 5 years experienced the greatest decline in cognition. Before CRT, growth hormone (GH) secretion abnormality was diagnosed in 24% of tested patients, and 12% had precocious puberty. The 10-year cumulative incidence of GH replacement was 48.9%; of thyroid hormone replacement, 64.0%; of glucocorticoid replacement, 19.2%; and of gonadotropin-releasing hormone analog therapy, 34.2%. The mean +/- standard errors of the cumulative incidence of hearing loss at 10 years did not exceed 5.7% +/- 3.3% at any frequency.
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the largest series of prospectively followed children with LGG to undergo irradiation. Adverse effects are limited and predictable for most patients; however, this study provides additional evidence that CRT should be delayed for young patients and identifies the potential benefits of reducing radiation dose to normal brain.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Marcus KJ, Goumnerova L, Billett AL, et al. Stereotactic radiotherapy for localized low-grade gliomas in children: Final results of a prospective trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;61:374–379. - PubMed
-
- Saran FH, Baumert BG, Khoo VS, et al. Stereotactically guided conformal radiotherapy for progressive low-grade gliomas of childhood. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;53:43–51. - PubMed
-
- Grabenbauer GG, Schuchardt U, Buchfelder M, et al. Radiation therapy of optico-hypothalamic gliomas (OHG)-radiographic response, vision and late toxicity. Radiother Oncol. 2000;54:239–245. - PubMed
-
- Erkal HS, Serin M, Cakmak A. Management of optic pathway and chiasmatic-hypothalamic gliomas in children with radiation therapy. Radiother Oncol. 1997;45:11–15. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

