Cellular inflammatory response to flaviviruses in the central nervous system of a primate host
- PMID: 19581627
- PMCID: PMC2746730
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.2009.954180
Cellular inflammatory response to flaviviruses in the central nervous system of a primate host
Abstract
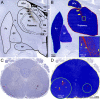
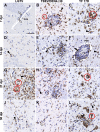
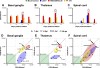
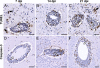
Flaviviruses such as tick-borne encephalitis virus, Japanese encephalitis virus, West Nile virus, and St. Louis encephalitis virus are important neurotropic human pathogens, typically causing a devastating and often fatal neuroinfection. Flaviviruses induce neuroinflammation with typical features of viral encephalitides, including inflammatory cell infiltration, activation of microglia, and neuronal degeneration. Development of safe and effective live-virus vaccines against neurotropic flavivirus infections demands a detailed knowledge of their neuropathogenesis in a primate host that is evolutionarily close to humans. Here, we used computerized morphometric analysis to quantitatively assess the cellular inflammatory responses in the central nervous system (CNS) of rhesus monkeys infected with three antigenically divergent attenuated flaviviruses. The kinetics, spatial pattern, and magnitude of microglial activation, trafficking of T and B cells, and changes in T cell subsets within the CNS define unique phenotypic signatures for each of the three viruses. Our results provide a benchmark for investigation of cellular inflammatory responses induced by attenuated flaviviruses in the CNS of primate hosts and provide insight into the neuropathogenesis of flavivirus encephalitis that might guide the development of safe and effective live-virus vaccines.
Figures






References
-
- Binder GK, Griffin DE (2001) Interferon-gamma-mediated site-specific clearance of alphavirus from CNS neurons. Science 293:303–306 - PubMed
-
- Bréhin AC, Mouries J, Frenkiel MP, Dadaglio G, Despres P, Lafon M, Couderc T (2008) Dynamics of immune cell recruitment during West Nile encephalitis and identification of a new CD19+B220-BST-2+ leukocyte population. J Immunol 180:6760–6767 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

