Dissecting an allosteric switch in caspase-7 using chemical and mutational probes
- PMID: 19581639
- PMCID: PMC2758006
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.001826
Dissecting an allosteric switch in caspase-7 using chemical and mutational probes
Abstract
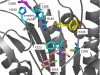
Apoptotic caspases, such as caspase-7, are stored as inactive protease zymogens, and when activated, lead to a fate-determining switch to induce cell death. We previously discovered small molecule thiol-containing inhibitors that when tethered revealed an allosteric site and trapped a conformation similar to the zymogen form of the enzyme. We noted three structural transitions that the compounds induced: (i) breaking of an interaction between Tyr-223 and Arg-187 in the allosteric site, which prevents proper ordering of the catalytic cysteine; (ii) pinning the L2' loop over the allosteric site, which blocks critical interactions for proper ordering of the substrate-binding groove; and (iii) a hinge-like rotation at Gly-188 positioned after the catalytic Cys-186 and Arg-187. Here we report a systematic mutational analysis of these regions to dissect their functional importance to mediate the allosteric transition induced by these compounds. Mutating the hinge Gly-188 to the restrictive proline causes a massive approximately 6000-fold reduction in catalytic efficiency. Mutations in the Arg-187-Tyr-223 couple have a far less dramatic effect (3-20-fold reductions). Interestingly, although the allosteric couple mutants still allow binding and allosteric inhibition, they partially relieve the mutual exclusivity of binding between inhibitors at the active and allosteric sites. These data highlight a small set of residues critical for mediating the transition from active to inactive zymogen-like states.
Figures
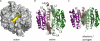





Similar articles
-
L2' loop is critical for caspase-7 active site formation.Protein Sci. 2009 Jul;18(7):1459-68. doi: 10.1002/pro.151. Protein Sci. 2009. PMID: 19530232 Free PMC article.
-
How do mutations and allosteric inhibitors modulate caspase-7 activity? A molecular dynamics study.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2019 Aug;37(13):3456-3466. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2018.1517611. Epub 2018 Nov 17. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2019. PMID: 30175666
-
Identification of Allosteric Inhibitors against Active Caspase-6.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 2;9(1):5504. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41930-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30940883 Free PMC article.
-
Searching for new allosteric sites in enzymes.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004 Dec;14(6):706-15. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2004.10.009. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2004. PMID: 15582395 Review.
-
Evolution of an allosteric "off switch" in apoptotic caspases.J Biol Chem. 2018 Apr 13;293(15):5462-5463. doi: 10.1074/jbc.H118.002379. J Biol Chem. 2018. PMID: 29654071 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Allosteric Tuning of Caspase-7: A Fragment-Based Drug Discovery Approach.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017 Nov 13;56(46):14443-14447. doi: 10.1002/anie.201706959. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017. PMID: 28940929 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Non-Catalytic Cysteine Residues Through Structure-Guided Drug Discovery.Curr Top Med Chem. 2017;17(1):4-15. doi: 10.2174/1568026616666160719163839. Curr Top Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27449257 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemoproteomics Using Nucleotide Acyl Phosphates Reveals an ATP Binding Site at the Dimer Interface of Procaspase-6.Biochemistry. 2019 Dec 31;58(52):5320-5328. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00290. Epub 2019 May 24. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31095371 Free PMC article.
-
A bifunctional allosteric site in the dimer interface of procaspase-3.Biophys Chem. 2011 Nov;159(1):100-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2011.05.013. Epub 2011 May 25. Biophys Chem. 2011. PMID: 21645959 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of tractable allosteric sites in G protein-coupled receptors.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 16;9(1):6180. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42618-8. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30992500 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

