The FLARE intraoperative near-infrared fluorescence imaging system: a first-in-human clinical trial in breast cancer sentinel lymph node mapping
- PMID: 19582506
- PMCID: PMC2772055
- DOI: 10.1245/s10434-009-0594-2
The FLARE intraoperative near-infrared fluorescence imaging system: a first-in-human clinical trial in breast cancer sentinel lymph node mapping
Abstract
Background: Invisible NIR fluorescent light can provide high sensitivity, high-resolution, and real-time image-guidance during oncologic surgery, but imaging systems that are presently available do not display this invisible light in the context of surgical anatomy. The FLARE imaging system overcomes this major obstacle.
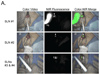
Methods: Color video was acquired simultaneously, and in real-time, along with two independent channels of NIR fluorescence. Grayscale NIR fluorescence images were converted to visible "pseudo-colors" and overlaid onto the color video image. Yorkshire pigs weighing 35 kg (n = 5) were used for final preclinical validation of the imaging system. A six-patient pilot study was conducted in women undergoing sentinel lymph node (SLN) mapping for breast cancer. Subjects received (99m)Tc-sulfur colloid lymphoscintigraphy. In addition, 12.5 microg of indocyanine green (ICG) diluted in human serum albumin (HSA) was used as an NIR fluorescent lymphatic tracer.
Results: The FLARE system permitted facile positioning in the operating room. NIR light did not change the look of the surgical field. Simultaneous pan-lymphatic and SLN mapping was demonstrated in swine using clinically available NIR fluorophores and the dual NIR capabilities of the system. In the pilot clinical trial, a total of nine SLNs were identified by (99m)Tc- lymphoscintigraphy and nine SLNs were identified by NIR fluorescence, although results differed in two patients. No adverse events were encountered.
Conclusions: We describe the successful clinical translation of a new NIR fluorescence imaging system for image-guided oncologic surgery.
Figures




References
-
- Frangioni JV. In vivo near-infrared fluorescence imaging. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2003;7:626–634. - PubMed
-
- Fujiwara M, Mizukami T, Suzuki A, Fukamizu H. Sentinel lymph node detection in skin cancer patients using real-time fluorescence navigation with indocyanine green: preliminary experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008 - PubMed
-
- Kitai T, Inomoto T, Miwa M, Shikayama T. Fluorescence navigation with indocyanine green for detecting sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 2005;12:211–215. - PubMed
-
- Ogasawara Y, Ikeda H, Takahashi M, Kawasaki K, Doihara H. Evaluation of breast lymphatic pathways with indocyanine green fluorescence imaging in patients with breast cancer. World J Surg. 2008;32:1924–1929. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

