Inhibition of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase by inhibitor SAM486A connects polyamine metabolism with p53-Mdm2-Akt/protein kinase B regulation and apoptosis in neuroblastoma
- PMID: 19584241
- PMCID: PMC2731875
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-08-1217
Inhibition of S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase by inhibitor SAM486A connects polyamine metabolism with p53-Mdm2-Akt/protein kinase B regulation and apoptosis in neuroblastoma
Abstract
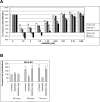
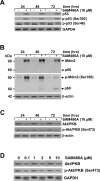
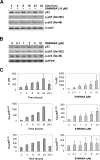
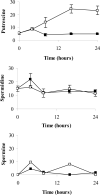
S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase (AdoMetDC) is an essential enzyme of polyamine (PA) biosynthesis, and both AdoMetDC and PA levels are often up-regulated in cancer cells. The second-generation inhibitor SAM486A inhibits AdoMetDC enzyme activity and has been evaluated in phase II clinical cancer trials. However, little is known about the mechanism of action and potential use of this therapeutic drug in the treatment of the pediatric cancer neuroblastoma (NB). Here, we show that p53 wild-type NB cells are highly sensitive to SAM486A treatment. Most notably, SAM486A treatment resulted in the rapid accumulation of proapoptotic proteins p53 and Mdm2. Concomitant with the increase of proteins at endogenous levels, the in vivo phosphorylation of p53 at residues Ser(46)/Ser(392) and Mdm2 at residue Ser(166) was observed. Moreover, the antiapoptotic protein Akt/protein kinase B was down-regulated and also dephosphorylated at residue Ser(473) in a dose- and time-dependent manner and NB cells entered apoptotic cell death. The results presented in this study highlight the importance of PA homeostasis and provide a direct link between PA metabolism and apoptotic cell signaling pathways in p53 wild-type NB cells. PA inhibitors such as SAM486A may be effective alternative agents for the treatment of NBs with or without MYCN amplification.
Figures

References
-
- Davidson NE, Hahm HA, McCloskey DE, Woster PM, Casero RA., Jr Clinical aspects of cell death in breast cancer: the polyamine pathway as a new target for treatment. Endocr Relat Cancer. 1999;6:69–73. - PubMed
-
- Levin VA, Hess KR, Choucair A, et al. Phase III randomized study of postradiotherapy chemotherapy with combination alpha-difluoromethylornithine-PCV versus PCV for anaplastic gliomas. Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9:981–90. - PubMed
-
- Levin VA, Uhm JH, Jaeckle KA, et al. Phase III randomized study of postradiotherapy chemotherapy with alpha-difluoromethylornithine-procarbazine, N-(2-chloroethyl)-N'-cyclohexyl-N-nitrosurea, vincristine (DFMO-PCV) versus PCV for glioblastoma multiforme. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:3878–84. - PubMed
-
- McCann PP, Pegg AE. Ornithine decarboxylase as an enzyme target for therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;54:195–215. - PubMed
-
- Meyskens FL, Jr, Gerner EW. Development of difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) as a chemoprevention agent. Clin Cancer Res. 1999;5:945–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

