Lipoproteins, cholesterol homeostasis and cardiac health
- PMID: 19584955
- PMCID: PMC2706428
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.5.474
Lipoproteins, cholesterol homeostasis and cardiac health
Abstract
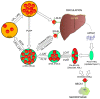
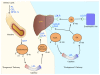
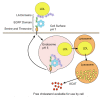
Cholesterol is an essential substance involved in many functions, such as maintaining cell membranes, manufacturing vitamin D on surface of the skin, producing hormones, and possibly helping cell connections in the brain. When cholesterol levels rise in the blood, they can, however, have dangerous consequences. In particular, cholesterol has generated considerable notoriety for its causative role in atherosclerosis, the leading cause of death in developed countries around the world. Homeostasis of cholesterol is centered on the metabolism of lipoproteins, which mediate transport of the lipid to and from tissues. As a synopsis of the major events and proteins that manage lipoprotein homeostasis, this review contributes to the substantial attention that has recently been directed to this area. Despite intense scrutiny, the majority of phenotypic variation in total cholesterol and related traits eludes explanation by current genetic knowledge. This is somewhat disappointing considering heritability estimates have established these traits as highly genetic. Thus, the continued search for candidate genes, mutations, and mechanisms is vital to our understanding of heart disease at the molecular level. Furthermore, as marker development continues to predict risk of vascular illness, this knowledge has the potential to revolutionize treatment of this leading human disease.
Keywords: HDL; Homeostasis; LDL; candidate genes; cholesterol; expression; heart disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures

References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M. et al.Heart disease and stroke statistics--2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2009;119:480–486. - PubMed
-
- Stamler J, Daviglus ML, Garside DB. et al.Relationship of baseline serum cholesterol levels in 3 large cohorts of younger men to long-term coronary, cardiovascular, and all-cause mortality and to longevity. JAMA. 2000;284:311–318. - PubMed
-
- Mourão PA, Bracamonte CA. The binding of human aortic glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans to plasma low density lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis. 1984;50:133–146. - PubMed
-
- Wilson PW, Abbott RD, Castelli WP. High density lipoprotein cholesterol and mortality. The Framingham Heart Study. Arteriosclerosis. 1988;8:737–741. - PubMed
-
- O'Connell DL, Heller RF, Roberts DC. et al.Twin study of genetic and environmental effects on lipid levels. Genet Epidemiol. 1988;5:323–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

