Water dynamics in large and small reverse micelles: from two ensembles to collective behavior
- PMID: 19586114
- PMCID: PMC2721765
- DOI: 10.1063/1.3159779
Water dynamics in large and small reverse micelles: from two ensembles to collective behavior
Abstract
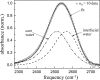
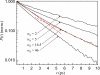
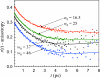
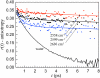
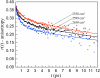
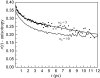
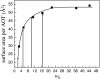
The dynamics of water in Aerosol-OT reverse micelles are investigated with ultrafast infrared spectroscopy of the hydroxyl stretch. In large reverse micelles, the dynamics of water are separable into two ensembles: slow interfacial water and bulklike core water. As the reverse micelle size decreases, the slowing effect of the interface and the collective nature of water reorientation begin to slow the dynamics of the core water molecules. In the smallest reverse micelles, these effects dominate and all water molecules have the same long time reorientational dynamics. To understand and characterize the transition in the water dynamics from two ensembles to collective reorientation, polarization and frequency selective infrared pump-probe experiments are conducted on the complete range of reverse micelle sizes from a diameter of 1.6-20 nm. The crossover between two ensemble and collective reorientation occurs near a reverse micelle diameter of 4 nm. Below this size, the small number of confined water molecules and structural changes in the reverse micelle interface leads to homogeneous long time reorientation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Water dynamics at neutral and ionic interfaces.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Sep 8;106(36):15243-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907875106. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19706895 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of water at the interface in reverse micelles: measurements of spectral diffusion with two-dimensional infrared vibrational echoes.J Phys Chem B. 2011 Oct 13;115(40):11658-70. doi: 10.1021/jp206903k. Epub 2011 Sep 22. J Phys Chem B. 2011. PMID: 21899355
-
Dynamics of nanoscopic water: vibrational echo and infrared pump-probe studies of reverse micelles.J Phys Chem B. 2005 Nov 17;109(45):21273-84. doi: 10.1021/jp051837p. J Phys Chem B. 2005. PMID: 16853758
-
Analysis of water in confined geometries and at interfaces.Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2010;3:89-107. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-070109-103410. Annu Rev Anal Chem (Palo Alto Calif). 2010. PMID: 20636035 Review.
-
Infrared spectroscopy of proteins in reverse micelles.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1828(10):2314-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.10.019. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23098833 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radical re-appraisal of water structure in hydrophilic confinement.Chem Phys Lett. 2013 Dec 18;590:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.cplett.2013.10.075. Chem Phys Lett. 2013. PMID: 25843963 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamics of Functionalized Surface Molecular Monolayers Studied with Ultrafast Infrared Vibrational Spectroscopy.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2012 Nov 8;116(44):23428-23440. doi: 10.1021/jp307677b. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2012. PMID: 23259027 Free PMC article.
-
Water dynamics in small reverse micelles in two solvents: two-dimensional infrared vibrational echoes with two-dimensional background subtraction.J Chem Phys. 2011 Feb 7;134(5):054512. doi: 10.1063/1.3532542. J Chem Phys. 2011. PMID: 21303143 Free PMC article.
-
Proton Traffic Jam: Effect of Nanoconfinement and Acid Concentration on Proton Hopping Mechanism.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021 Nov 22;60(48):25419-25427. doi: 10.1002/anie.202108766. Epub 2021 Oct 4. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2021. PMID: 34402145 Free PMC article.
-
Water dynamics at neutral and ionic interfaces.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Sep 8;106(36):15243-8. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0907875106. Epub 2009 Aug 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009. PMID: 19706895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zulauf M. and Eicke H. -F., J. Phys. Chem. JPCHAX 83, 480 (1979).10.1021/j100467a011 - DOI
-
- Kinugasa T., Kondo A., Nishimura S., Miyauchi Y., Nishii Y., Watanabe K., and Takeuchi H., Colloids Surf., A CPEAEH 204, 193 (2002).10.1016/S0927-7757(01)01132-3 - DOI
-
- Eicke H. -F. and Rehak J., Helv. Chim. Acta HCACAV 59, 2883 (1976).10.1002/hlca.19760590825 - DOI
-
- Grigolini P. and Maestro M., Chem. Phys. Lett. CHPLBC 127, 248 (1986).10.1016/0009-2614(86)80267-6 - DOI
-
- Quist P. -O. and Halle B., J. Chem. Soc., Faraday Trans. 1 JCFTAR 84, 1033 (1988).10.1039/f19888401033 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

