Transforming growth factor beta promotes neuronal cell fate of mouse cortical and hippocampal progenitors in vitro and in vivo: identification of Nedd9 as an essential signaling component
- PMID: 19587023
- PMCID: PMC2820705
- DOI: 10.1093/cercor/bhp134
Transforming growth factor beta promotes neuronal cell fate of mouse cortical and hippocampal progenitors in vitro and in vivo: identification of Nedd9 as an essential signaling component
Abstract
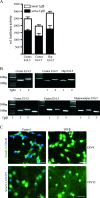
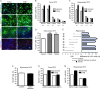
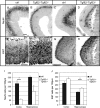
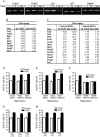
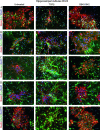
Transforming Growth Factor beta (Tgfbeta) and associated signaling effectors are expressed in the forebrain, but little is known about the role of this multifunctional cytokine during forebrain development. Using hippocampal and cortical primary cell cultures of developing mouse brains, this study identified Tgfbeta-regulated genes not only associated with cell cycle exit of progenitors but also with adoption of neuronal cell fate. Accordingly, we observed not only an antimitotic effect of Tgfbeta on progenitors but also an increased expression of neuronal markers in Tgfbeta treated cultures. This effect was dependent upon Smad4. Furthermore, in vivo loss-of-function analyses using Tgfbeta2(-/-)/Tgfbeta3(-/-) double mutant mice showed the opposite effect of increased cell proliferation and fewer neurons in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus. Gata2, Runx1, and Nedd9 were candidate genes regulated by Tgfbeta and known to be involved in developmental processes of neuronal progenitors. Using siRNA-mediated knockdown, we identified Nedd9 as an essential signaling component for the Tgfbeta-dependent increase in neuronal cell fate. Expression of this scaffolding protein, which is mainly described as a signaling molecule of the beta1-integrin pathway, was not only induced after Tgfbeta treatment but was also associated with morphological changes of the Nestin-positive progenitor pool observed upon exposure to Tgfbeta.
Figures
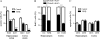
References
-
- Abe M, Harpel JG, Metz CN, Nunes I, Loskutoff DJ, Rifkin DB. An assay for transforming growth factor-beta using cells transfected with a plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 promoter-luciferase construct. Anal Biochem. 1994;216:276–284. - PubMed
-
- Abramova N, Charniga C, Goderie SK, Temple S. Stage-specific changes in gene expression in acutely isolated mouse CNS progenitor cells. Dev Biol. 2005;283:269–281. - PubMed
-
- Aquino JB, Marmigere F, Lallemend F, Lundgren TK, Villar MJ, Wegner M, Ernfors P. Differential expression and dynamic changes of murine NEDD9 in progenitor cells of diverse tissues. Gene Expr Patterns. 2008;8:217–226. - PubMed
-
- Brionne TC, Tesseur I, Masliah E, Wyss-Coray T. Loss of TGF-beta 1 leads to increased neuronal cell death and microgliosis in mouse brain. Neuron. 2003;40:1133–1145. - PubMed
-
- Chapuis J, Moisan F, Mellick G, Elbaz A, Silburn P, Pasquier F, Hannequin D, Lendon C, Campion D, Amouyel P, et al. Association study of the NEDD9 gene with the risk of developing Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:2863–2867. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

