Stepwise acquisition of pyrimethamine resistance in the malaria parasite
- PMID: 19587242
- PMCID: PMC2715478
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0905922106
Stepwise acquisition of pyrimethamine resistance in the malaria parasite
Abstract
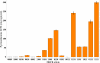
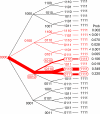
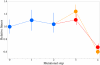
The spread of high-level pyrimethamine resistance in Africa threatens to curtail the therapeutic lifetime of antifolate antimalarials. We studied the possible evolutionary pathways in the evolution of pyrimethamine resistance using an approach in which all possible mutational intermediates were created by site-directed mutagenesis and assayed for their level of drug resistance. The coding sequence for dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) from the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum was mutagenized, and tests were carried out in Escherichia coli under conditions in which the endogenous bacterial enzyme was selectively inhibited. We studied 4 key amino acid replacements implicated in pyrimethamine resistance: N51I, C59R, S108N, and I164L. Using empirical estimates of the mutational spectrum in P. falciparum and probabilities of fixation based on the relative levels of resistance, we found that the predicted favored pathways of drug resistance are consistent with those reported in previous kinetic studies, as well as DHFR polymorphisms observed in natural populations. We found that 3 pathways account for nearly 90% of the simulated realizations of the evolution of pyrimethamine resistance. The most frequent pathway (S108N and then C59R, N51I, and I164L) accounts for more than half of the simulated realizations. Our results also suggest an explanation for why I164L is detected in Southeast Asia and South America, but not at significant frequencies in Africa.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Wellems TE. Plasmodium chloroquine resistance and the search for a replacement antimalarial drug. Science. 2002;198:124–126. - PubMed
-
- Looareesuwan S, et al. Clinical studies of atovaquone, alone or in combination with other antimalarial drugs, for treatment of acute uncomplicated malaria in Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1996;54:62–66. - PubMed
-
- Snewin VA, England SM, Sims PFG, Hyde JE. Characterisation of the dihydrofolate reductase–thymidylate synthetase gene from human malaria parasites highly resistant to pyrimethamine. Gene. 1989;76:41–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

