Alpha-latrotoxin stimulates a novel pathway of Ca2+-dependent synaptic exocytosis independent of the classical synaptic fusion machinery
- PMID: 19587270
- PMCID: PMC2739239
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0898-09.2009
Alpha-latrotoxin stimulates a novel pathway of Ca2+-dependent synaptic exocytosis independent of the classical synaptic fusion machinery
Abstract
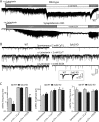
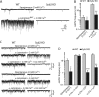
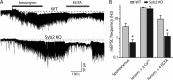
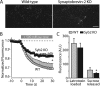
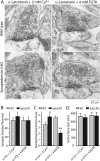
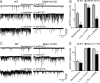
Alpha-latrotoxin induces neurotransmitter release by stimulating synaptic vesicle exocytosis via two mechanisms: (1) A Ca(2+)-dependent mechanism with neurexins as receptors, in which alpha-latrotoxin acts like a Ca(2+) ionophore, and (2) a Ca(2+)-independent mechanism with CIRL/latrophilins as receptors, in which alpha-latrotoxin directly stimulates the transmitter release machinery. Here, we show that the Ca(2+)-independent release mechanism by alpha-latrotoxin requires the synaptic SNARE-proteins synaptobrevin/VAMP and SNAP-25, and, at least partly, the synaptic active-zone protein Munc13-1. In contrast, the Ca(2+)-dependent release mechanism induced by alpha-latrotoxin does not require any of these components of the classical synaptic release machinery. Nevertheless, this type of exocytotic neurotransmitter release appears to fully operate at synapses, and to stimulate exocytosis of the same synaptic vesicles that participate in physiological action potential-triggered release. Thus, synapses contain two parallel and independent pathways of Ca(2+)-triggered exocytosis, a classical, physiological pathway that operates at the active zone, and a novel reserve pathway that is recruited only when Ca(2+) floods the synaptic terminal.
Figures

References
-
- Ádám-Vizi V, Déri Z, Bors P, Tretter L. Lack of involvement of [Ca2+]i in the external Ca2+-independent release of acetylcholine evoked by veratridine, ouabain and alpha-latrotoxin: possible role of [Na+]i . J Physiol Paris. 1993;87:43–50. - PubMed
-
- Augustin I, Rosenmund C, Südhof TC, Brose N. Munc13-1 is essential for fusion competence of glutamatergic synaptic vesicles. Nature. 1999;400:457–461. - PubMed
-
- Bronk P, Deák F, Wilson MC, Liu X, Südhof TC, Kavalali ET. Differential effects of SNAP-25 deletion on Ca2+-dependent and Ca2+-independent neurotransmission. J Neurophysiol. 2007;98:794–806. - PubMed
-
- Brose N, Hofmann K, Hata Y, Südhof TC. Mammalian homologues of Caenorhabditis elegans unc-13 gene define novel family of C2-domain proteins. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:25273–25280. - PubMed
-
- Capogna M, Gähwiler BH, Thompson SM. Calcium-independent actions of α-latrotoxin on spontaneous and evoked synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1996;76:3149–3158. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
