The gad2 promoter is a transcriptional target of estrogen receptor (ER)alpha and ER beta: a unifying hypothesis to explain diverse effects of estradiol
- PMID: 19587286
- PMCID: PMC2748993
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1289-09.2009
The gad2 promoter is a transcriptional target of estrogen receptor (ER)alpha and ER beta: a unifying hypothesis to explain diverse effects of estradiol
Abstract
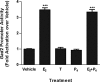
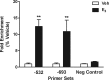
Estradiol (E(2)) regulates a wide range of neural functions, many of which require activation of estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and/or ERbeta, ligand-gated transcriptional regulators. Surprisingly, very few neural gene targets of ERs have been identified, and these cannot easily explain the myriad effects of E(2). GABA regulates most of the same neural functions as E(2), and GABAergic neurons throughout the brain contain ER. Therefore, we examined whether E(2) directly regulates expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase 2 (gad2), the enzyme primarily responsible for GABA synthesis for synaptic release. Using dual luciferase assays, we found that E(2), but not other gonadal steroids, stimulated the activity of a 2691 bp rat gad2 promoter reporter construct. Activation required either ERalpha or ERbeta, and ERbeta did not repress ERalpha-mediated transactivation. Site-directed mutagenesis studies identified three estrogen response elements (EREs) with cell-specific functions. An ERE at -711 upstream of the gad2 translational start site was essential for transactivation in both MCF-7 breast cancer cells and SN56.B5.G4 neural cells, but an ERE at -546 enhanced transcription only in neural cells. A third ERE at -1958 was inactive in neural cells but exerted potent transcriptional repression in E(2)-treated MCF-7 cells. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays in mouse GABAergic N42 cells confirmed that E(2) induced ERalpha binding to a DNA fragment containing sequences corresponding to the -546 and -711 EREs of the rat promoter. Based on these data, we propose that direct transcriptional regulation of gad2 may explain, at least in part, the ability of E(2) to impact such a diverse array of neural functions.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Oestrogen receptors pathways to oestrogen responsive elements: the transactivation function-1 acts as the keystone of oestrogen receptor (ER)beta-mediated transcriptional repression of ERalpha.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007 May;104(3-5):110-22. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.03.002. Epub 2007 Mar 12. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17478088
-
Estrogen receptor (ER)-mediated transcriptional regulation of the human corticotropin-releasing hormone-binding protein promoter: differential effects of ERalpha and ERbeta.Mol Endocrinol. 2004 Dec;18(12):2908-23. doi: 10.1210/me.2003-0446. Epub 2004 Sep 2. Mol Endocrinol. 2004. PMID: 15345745
-
Transcriptional regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor by estradiol and tamoxifen in breast cancer cells: a complex interplay between estrogen receptors alpha and beta.Cancer Res. 2002 Sep 1;62(17):4977-84. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 12208749
-
What's new in estrogen receptor action in the female reproductive tract.J Mol Endocrinol. 2016 Feb;56(2):R55-71. doi: 10.1530/JME-15-0254. J Mol Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26826253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ovarian hormone estradiol plays a crucial role in the control of food intake in females.Physiol Behav. 2011 Sep 26;104(4):517-24. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.04.014. Epub 2011 Apr 20. Physiol Behav. 2011. PMID: 21530561 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glutamatergic and GABAergic neurons in the preoptic area of the hypothalamus play key roles in menopausal hot flashes.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Oct 14;14:993955. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.993955. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36313017 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-specific Behavioral Features of Rodent Models of Autism Spectrum Disorder.Exp Neurobiol. 2018 Oct;27(5):321-343. doi: 10.5607/en.2018.27.5.321. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Exp Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 30429643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GABAergic influence on temporomandibular joint-responsive spinomedullary neurons depends on estrogen status.Neuroscience. 2014 Feb 14;259:53-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.11.053. Epub 2013 Dec 4. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24316475 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Action of Multitarget 7-Aminophenanthridin-6(5H)-one Derivatives against Metal-Induced Cell Death and Oxidative Stress in SN56 Cells.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021 Sep 15;12(18):3358-3372. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.1c00333. Epub 2021 Aug 30. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34460227 Free PMC article.
-
Resting state alpha frequency is associated with menstrual cycle phase, estradiol and use of oral contraceptives.Brain Res. 2014 Aug 19;1577(100):36-44. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.06.034. Epub 2014 Jul 7. Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 25010817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Andò S, De Amicis F, Rago V, Carpino A, Maggiolini M, Panno ML, Lanzino M. Breast cancer: from estrogen to androgen receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002;193:121–128. - PubMed
-
- Blurton-Jones M, Tuszynski MH. Estrogen receptor-beta colocalizes extensively with parvalbumin-labeled inhibitory neurons in the cortex, amygdala, basal forebrain, and hippocampal formation of intact and ovariectomized adult rats. J Comp Neurol. 2002;452:276–287. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
