Coexpression of the type 2 diabetes susceptibility gene variants KCNJ11 E23K and ABCC8 S1369A alter the ATP and sulfonylurea sensitivities of the ATP-sensitive K(+) channel
- PMID: 19587354
- PMCID: PMC2750221
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-0143
Coexpression of the type 2 diabetes susceptibility gene variants KCNJ11 E23K and ABCC8 S1369A alter the ATP and sulfonylurea sensitivities of the ATP-sensitive K(+) channel
Abstract
Objective: In the pancreatic beta-cell, ATP-sensitive K(+) (K(ATP)) channels couple metabolism with excitability and consist of Kir6.2 and SUR1 subunits encoded by KCNJ11 and ABCC8, respectively. Sulfonylureas, which inhibit the K(ATP) channel, are used to treat type 2 diabetes. Rare activating mutations cause neonatal diabetes, whereas the common variants, E23K in KCNJ11 and S1369A in ABCC8, are in strong linkage disequilibrium, constituting a haplotype that predisposes to type 2 diabetes. To date it has not been possible to establish which of these represents the etiological variant, and functional studies are inconsistent. Furthermore, there have been no studies of the S1369A variant or the combined effect of the two on K(ATP) channel function.
Research design and methods: The patch-clamp technique was used to study the nucleotide sensitivity and sulfonylurea inhibition of recombinant human K(ATP) channels containing either the K23/A1369 or E23/S1369 variants.
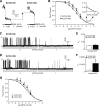
Results: ATP sensitivity of the K(ATP) channel was decreased in the K23/A1369 variant (half-maximal inhibitory concentration [IC(50)] = 8.0 vs. 2.5 mumol/l for the E23/S1369 variant), although there was no difference in ADP sensitivity. The K23/A1369 variant also displayed increased inhibition by gliclazide, an A-site sulfonylurea drug (IC(50) = 52.7 vs. 188.7 nmol/l for the E23/S1369 variant), but not by glibenclamide (AB site) or repaglinide (B site).
Conclusions: Our findings indicate that the common K23/A1369 variant K(ATP) channel displays decreased ATP inhibition that may contribute to the observed increased risk for type 2 diabetes. Moreover, the increased sensitivity of the K23/A1369 variant to the A-site sulfonylurea drug gliclazide may provide a pharmacogenomic therapeutic approach for patients with type 2 diabetes who are homozygous for both risk alleles.
Figures
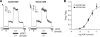


References
-
- Bryan J, Munoz A, Zhang X, Dufer M, Drews G, Krippeit-Drews P, Aguilar-Bryan L: ABCC8 and ABCC9: ABC transporters that regulate K+ channels. Pflugers Arch 2007;453:703–718 - PubMed
-
- Bryan J, Crane A, Vila-Carriles WH, Babenko AP, Aguilar-Bryan L: Insulin secretagogues, sulfonylurea receptors and KATP channels. Curr Pharm Des 2005;11:2699–2716 - PubMed
-
- Babenko AP, Polak M, Cave H, Busiah K, Czernichow P, Scharfmann R, Bryan J, Aguilar-Bryan L, Vaxillaire M, Froguel P: Activating mutations in the ABCC8 gene in neonatal diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 2006;355:456–466 - PubMed
-
- Gloyn AL, Pearson ER, Antcliff JF, Proks P, Bruining GJ, Slingerland AS, Howard N, Srinivasan S, Silva JM, Molnes J, Edghill EL, Frayling TM, Temple IK, Mackay D, Shield JP, Sumnik Z, van Rhijn A, Wales JK, Clark P, Gorman S, Aisenberg J, Ellard S, Njolstad PR, Ashcroft FM, Hattersley AT: Activating mutations in the gene encoding the ATP-sensitive potassium-channel subunit Kir6.2 and permanent neonatal diabetes. N Engl J Med 2004;350:1838–1849 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

