Improvement of sciatic nerve regeneration using laminin-binding human NGF-beta
- PMID: 19587785
- PMCID: PMC2703785
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0006180
Improvement of sciatic nerve regeneration using laminin-binding human NGF-beta
Abstract
Background: Sciatic nerve injuries often cause partial or total loss of motor, sensory and autonomic functions due to the axon discontinuity, degeneration, and eventual death which finally result in substantial functional loss and decreased quality of life. Nerve growth factor (NGF) plays a critical role in peripheral nerve regeneration. However, the lack of efficient NGF delivery approach limits its clinical applications. We reported here by fusing with the N-terminal domain of agrin (NtA), NGF-beta could target to nerve cells and improve nerve regeneration.
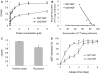
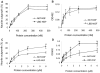
Methods: Laminin-binding assay and sustained release assay of NGF-beta fused with NtA (LBD-NGF) from laminin in vitro were carried out. The bioactivity of LBD-NGF on laminin in vitro was also measured. Using the rat sciatic nerve crush injury model, the nerve repair and functional restoration by utilizing LBD-NGF were tested.
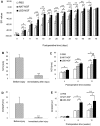
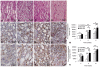
Findings: LBD-NGF could specifically bind to laminin and maintain NGF activity both in vitro and in vivo. In the rat sciatic nerve crush injury model, we found that LBD-NGF could be retained and concentrated at the nerve injury sites to promote nerve repair and enhance functional restoration following nerve damages.
Conclusion: Fused with NtA, NGF-beta could bind to laminin specifically. Since laminin is the major component of nerve extracellular matrix, laminin binding NGF could target to nerve cells and improve the repair of peripheral nerve injuries.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kline DG, Kim D, Midha R, Harsh C, Tiel R. Management and results of sciatic nerve injuries: a 24-year experience. J Neurosurg. 1998;89:13–23. - PubMed
-
- Korompilias AV, Payatakes AH, Beris AE, Vekris MD, Afendras GD, et al. Sciatic and peroneal nerve injuries. Microsurgery. 2006;26:288–294. - PubMed
-
- Navarro X, Vivo M, Valero-Cabre A. Neural plasticity after peripheral nerve injury and regeneration. Prog Neurobiol. 2007;82:163–201. - PubMed
-
- Rosberg HE, Carlsson KS, Dahlin LB. Prospective study of patients with injuries to the hand and forearm: costs, function, and general health. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg. 2005;39:360–369. - PubMed
-
- Lundborg G. A 25-year perspective of peripheral nerve surgery: evolving neuroscientific concepts and clinical significance. J Hand Surg [Am] 2000;25:391–414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

