Muscle-specific receptor tyrosine kinase antibody positive myasthenia gravis current status
- PMID: 19587811
- PMCID: PMC2706412
- DOI: 10.3988/jcn.2009.5.2.53
Muscle-specific receptor tyrosine kinase antibody positive myasthenia gravis current status
Abstract
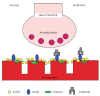
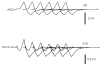
Muscle-specific tyrosine-kinase-antibody-positive myasthenia gravis (MuSK-MG) has emerged as a distinct entity since 2001. This disease has been reported worldwide, but with varying rates among patients with generalized acetylcholine-receptor-antibody-negative MG. MuSK-MG was detected in approximately 37% of generalized acetylcholine receptor antibody-negative MG. MuSK-MG patients were predominantly female with more prominent facial and bulbar involvement and more frequent crises. Disease onset tended to be earlier. Patients tended to have a relatively poor edrophonium response but showed prominent decrement in the repetitive nerve stimulation test in the facial muscles. Patients were more likely to display poor tolerance of, or a lack of improvement with, anticholinesterase agents. Somewhat better response was observed with steroids and plasma exchange. Most were managed successfully with aggressive immunomodulatory therapies, although a higher proportion of MuSK-MG patients had a refractory course when compared with other forms of generalized MG. I present here an up-to-date overview on MuSK-MG based on our experience at the University of Alabama at Birmingham and the existing literature.
Keywords: muscle-specific tyrosine-kinase-antibody; myasthenia gravis; seronegative myasthenia gravis.
Figures
References
-
- Simpson JA. Myasthenia gravis: a new hypothesis. Scott Med J. 1960;5:419–436. - PubMed
-
- Lindstrom JM, Seybold ME, Lennon VA, Whittingham S, Duane DD. Antibody to acetylcholine receptor in myasthenia gravis. Prevalence, clinical correlates, and diagnostic value. Neurology. 1976;26:1054–1059. - PubMed
-
- Hoch W, McConville J, Helms S, Newsom-Davis J, Melms A, Vincent A. Auto-antibodies to the receptor tyrosine kinsase MuSK in patients with myasthenia gravis, without acetylcholine receptor antibodies. Nat Med. 2001;7:365–368. - PubMed
-
- Soliven BC, Lange DJ, Penn AS, Younger D, Jeretzki A, 3rd, Lovelace RE, et al. Seronegative maysthenia gravis. Neurology. 1988;38:514–517. - PubMed
-
- Oh SJ. Electrophysiological characteristics in seronegative myasthenia gravis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993;681:584–587. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

