Selective upregulation of interleukin-8 by human rhabdomyosarcomas in response to hypoxia: therapeutic implications
- PMID: 19588509
- PMCID: PMC4021846
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.24732
Selective upregulation of interleukin-8 by human rhabdomyosarcomas in response to hypoxia: therapeutic implications
Abstract
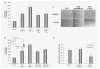
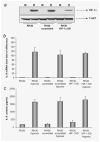
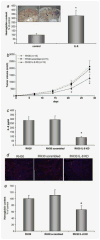
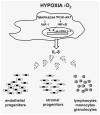
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is the most common soft-tissue sarcoma of adolescence and childhood. Because RMS tumors are highly vascularized, we sought to determine which factors secreted by RMS cells are crucial in stimulating angiogenesis in response to hypoxia. To address this issue, we evaluated expression of several proangiogenic factors [interleukin (IL)-8, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-2, stromal-derived factor (SDF)-1, hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF)] in 8 human RMS cell lines in both normal steady-state and hypoxic conditions. We found by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RQ-PCR) and confirmed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) that from all the factors evaluated, IL-8, whose expression is very low in normoxia, had been very highly expressed and secreted by RMS cells lines during hypoxic conditions ( approximately 40-170 times). Interestingly, this upregulation was not affected by knocking down hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha, but was inhibited by mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)p42/44 and phosphatidylinositaol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway inhibitors. This suggests that IL-8 expression is regulated in an activating protein (AP)-1- and nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB-dependent manner. Furthermore, we found that conditioned media (CM) harvested from RMS cells exposed to hypoxia activated and stimulated chemotactic responses in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and that IL-8 was responsible for hypoxia-related effects. Finally, by employing shRNA, the expression of IL-8 in human RH-30 cells was downregulated. We noticed that such RMS cells, if injected into skeletal muscles of immunodeficient mice, have a reduced ability for tumor formation. We conclude that IL-8 is a pivotal proangiogenic factor released by human RMS cells in hypoxic conditions and that the targeting of IL-8 may prove to be a novel and efficient strategy for inhibiting RMS growth.
Figures


References
-
- Barr FG, Galili N, Holick J, Biegel JA, Rovera G, Emanuel BS. Rearrangement of the PAX3 paired box gene in the paediatric solid tumour alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Nature Genet. 1993;3:113–117. - PubMed
-
- Bennicelli JL, Advani S, Schafer BW, Barr FG. PAX3 and PAX7 exhibit conserved cis-acting transcription repression domains and utilize a common gain of function mechanism in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Oncogene. 1999;18:4348–4356. - PubMed
-
- Collins MH, Zhao H, Womer RB, Barr FG. Proliferative and apoptotic differences between alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma subtypes: a comparative study of tumors containing PAX3-FKHR or PAX7-FKHR gene fusions. Med Ped Oncol. 2001;37:83–89. - PubMed
-
- Davis RJ, D’Cruz CM, Lovell MA, Biegel JA, Barr FG. Fusion of PAX7 to FKHR by the variant t(1;13)(p36;q14) translocation in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res. 1994;54:2869–2872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

