DAI/ZBP1 recruits RIP1 and RIP3 through RIP homotypic interaction motifs to activate NF-kappaB
- PMID: 19590578
- PMCID: PMC2726668
- DOI: 10.1038/embor.2009.109
DAI/ZBP1 recruits RIP1 and RIP3 through RIP homotypic interaction motifs to activate NF-kappaB
Abstract
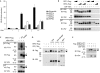
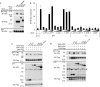
Detection of viral nucleic acids is central to antiviral immunity. Recently, DAI/ZBP1 (DNA-dependent activator of IRFs/Z-DNA binding protein 1) was identified as a cytoplasmic DNA sensor and shown to activate the interferon regulatory factor (IRF) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) transcription factors, leading to type-I interferon production. DAI-induced IRF activation depends on TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1), whereas signalling pathways and molecular components involved in NF-kappaB activation remain elusive. Here, we report the identification of two receptor-interacting protein (RIP) homotypic interaction motifs (RHIMs) in the DAI protein sequence, and show that these domains relay DAI-induced NF-kappaB signals through the recruitment of the RHIM-containing kinases RIP1 and RIP3. We show that knockdown of not only RIP1, but also RIP3 affects DAI-induced NF-kappaB activation. Importantly, RIP recruitment to DAI is inhibited by the RHIM-containing murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV) protein M45. These findings delineate the DAI signalling pathway to NF-kappaB and suggest a possible new immune modulation strategy of the MCMV.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Brune W, Menard C, Heesemann J, Koszinowski UH (2001) A ribonucleotide reductase homolog of cytomegalovirus and endothelial cell tropism. Science 291: 303–305 - PubMed
-
- Burckstummer T et al. (2009) An orthogonal proteomic-genomic screen identifies AIM2 as a cytoplasmic DNA sensor for the inflammasome. Nat Immunol 10: 266–272 - PubMed
-
- Ishii KJ et al. (2006) A Toll-like receptor-independent antiviral response induced by double-stranded B-form DNA. Nat Immunol 7: 40–48 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

