Effects of stimulus font and size on masked repetition priming: An event-related potentials (ERP) investigation
- PMID: 19590754
- PMCID: PMC2707185
- DOI: 10.1080/01690960701579839
Effects of stimulus font and size on masked repetition priming: An event-related potentials (ERP) investigation
Abstract
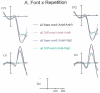
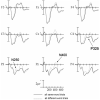
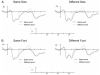
The size and font of target words were manipulated in a masked repetition priming paradigm with ERP recordings. Repetition priming effects were found in four ERP components: the N/P150, N250, P325, and N400. Neither a change in font nor a change in size across prime and target were found to affect repetition priming in the N250, P325, and N400 components. Changing font was, however, found to affect repetition priming in the N/P150 component, while the interaction between repetition priming and size was not significant in this component. These results confirm our interpretation of the N/P150 as a component sensitive to feature-level processing, and suggest that the type of prelexical and lexical processing reflected in the N250, P325, and N400 components is performed on representations that are invariant to changes in both font and size.
Figures


References
-
- Bentin S, Mouchetant-Rostaing Y, Giard MH, Echallier JF, Pernier J. ERP manifestations of processing printed words at different psycholinguistic levels: Time course and scalp distribution. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 1999;11:235–260. - PubMed
-
- Caramazza A, Hillis AE. Spatial representation of words in the brain implied by studies of a unilateral neglect patient. Nature. 1990;346:267–269. - PubMed
-
- Cohen L, Dehaene S, Naccache L, Lehéricy S, Dehaene-Lambertz G, Hénaff MA, Michel F. The visual word form area: Spatial and temporal characterization of an initial stage of reading in normal subjects and posterior split-brain patients. Brain. 2000;123:291–307. - PubMed
-
- Cornelissen P, Tarkiainen A, Helenius P, Salmelin R. Cortical effects of shifting letter position in letter strings of varying length. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience. 2003;15:731–746. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
