Receptor for advanced glycation end products is detrimental during influenza A virus pneumonia
- PMID: 19592063
- PMCID: PMC4540231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2009.05.032
Receptor for advanced glycation end products is detrimental during influenza A virus pneumonia
Abstract
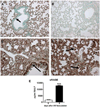
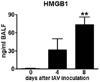
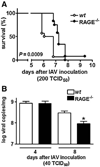
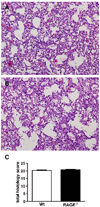
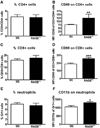
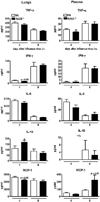
Pneumonia caused by influenza A virus (IAV) can have devastating effects, resulting in respiratory failure and death. The idea that a new influenza pandemic might occur in the near future has triggered renewed interests in IAV infection. The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) is expressed on different cell types and plays a key role in diverse inflammatory processes. We here investigated the role of RAGE in the host response to IAV pneumonia using wild-type (wt) and RAGE deficient ((-/-)) mice. Whereas strong RAGE was constitutively expressed in the lungs of uninfected wt mice, in particular on endothelium, IAV pneumonia was associated with enhanced expression on endothelium and de novo expression on bronchial epithelium. Additionally, the high-affinity RAGE ligand high mobility group box 1 was upregulated during IAV pneumonia. RAGE(-/-) mice were relatively protected from IAV induced mortality and showed an improved viral clearance and enhanced cellular T cell response and activation of neutrophils. These data suggest that RAGE is detrimental during IAV pneumonia.
Figures
References
-
- Alcami A, Smith GL. Receptors for gamma-interferon encoded by poxviruses: implications for the unknown origin of vaccinia virus. Trends Microbiol. 1996;4:321–326. - PubMed
-
- Allan W, Tabi Z, Cleary A, Doherty PC. Cellular events in the lymph node and lung of mice with influenza. Consequences of depleting CD4+ T cells. J. Immunol. 1990;144:3980–3986. - PubMed
-
- Arumugam T, Simeone DM, Schmidt AM, Logsdon CD. S100P stimulates cell proliferation and survival via receptor for activated glycation end products (RAGE) J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:5059–5065. - PubMed
-
- Bierhaus A, Stern DM, Nawroth PP. RAGE in inflammation: a new therapeutic target? Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2006;7:985–991. - PubMed
-
- Cataldegirmen G, Zeng S, Feirt N, Ippagunta N, Dun H, Qu W, Lu Y, Rong LL, Hofmann MA, Kislinger T, Pachydaki SI, Jenkins DG, Weinberg A, Lefkowitch J, Rogiers X, Yan SF, Schmidt AM, Emond JC. RAGE limits regeneration after massive liver injury by coordinated suppression of TNF-alpha and NF-kappaB. J. Exp. Med. 2005;201:473–484. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

