Computational identification of potential molecular interactions in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 19592425
- PMCID: PMC2735983
- DOI: 10.1104/pp.109.141317
Computational identification of potential molecular interactions in Arabidopsis
Abstract
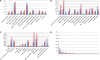
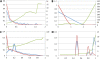
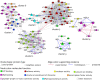
Knowledge of the protein interaction network is useful to assist molecular mechanism studies. Several major repositories have been established to collect and organize reported protein interactions. Many interactions have been reported in several model organisms, yet a very limited number of plant interactions can thus far be found in these major databases. Computational identification of potential plant interactions, therefore, is desired to facilitate relevant research. In this work, we constructed a support vector machine model to predict potential Arabidopsis (Arabidopsis thaliana) protein interactions based on a variety of indirect evidence. In a 100-iteration bootstrap evaluation, the confidence of our predicted interactions was estimated to be 48.67%, and these interactions were expected to cover 29.02% of the entire interactome. The sensitivity of our model was validated with an independent evaluation data set consisting of newly reported interactions that did not overlap with the examples used in model training and testing. Results showed that our model successfully recognized 28.91% of the new interactions, similar to its expected sensitivity (29.02%). Applying this model to all possible Arabidopsis protein pairs resulted in 224,206 potential interactions, which is the largest and most accurate set of predicted Arabidopsis interactions at present. In order to facilitate the use of our results, we present the Predicted Arabidopsis Interactome Resource, with detailed annotations and more specific per interaction confidence measurements. This database and related documents are freely accessible at http://www.cls.zju.edu.cn/pair/.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PAIR: the predicted Arabidopsis interactome resource.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(Database issue):D1134-40. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq938. Epub 2010 Oct 15. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 20952401 Free PMC article.
-
The predicted Arabidopsis interactome resource and network topology-based systems biology analyses.Plant Cell. 2011 Mar;23(3):911-22. doi: 10.1105/tpc.110.082529. Epub 2011 Mar 25. Plant Cell. 2011. PMID: 21441435 Free PMC article.
-
A predicted interactome for Arabidopsis.Plant Physiol. 2007 Oct;145(2):317-29. doi: 10.1104/pp.107.103465. Epub 2007 Aug 3. Plant Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17675552 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis bioinformatics: tools and strategies.Plant J. 2021 Dec;108(6):1585-1596. doi: 10.1111/tpj.15547. Epub 2021 Nov 9. Plant J. 2021. PMID: 34695270 Review.
-
Meiotic chromosome synapsis and recombination in Arabidopsis thaliana: new ways of integrating cytological and molecular approaches.Chromosome Res. 2014 Jun;22(2):179-90. doi: 10.1007/s10577-014-9426-8. Chromosome Res. 2014. PMID: 24941912 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in omics and bioinformatics tools for systems analyses of plant functions.Plant Cell Physiol. 2011 Dec;52(12):2017-38. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcr153. Plant Cell Physiol. 2011. PMID: 22156726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mapping plant interactomes using literature curated and predicted protein-protein interaction data sets.Plant Cell. 2010 Apr;22(4):997-1005. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.072736. Epub 2010 Apr 6. Plant Cell. 2010. PMID: 20371643 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide functional association networks: background, data & state-of-the-art resources.Brief Bioinform. 2020 Jul 15;21(4):1224-1237. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz064. Brief Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 31281921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the Arabidopsis floral transition process by integrating a protein-protein interaction network and gene expression data.Plant Physiol. 2010 Aug;153(4):1492-505. doi: 10.1104/pp.110.153650. Epub 2010 Jun 7. Plant Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20530214 Free PMC article.
-
PRIN: a predicted rice interactome network.BMC Bioinformatics. 2011 May 16;12:161. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-161. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011. PMID: 21575196 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alvarez-Venegas R, Pien S, Sadder M, Witmer X, Grossniklaus U, Avramova Z (2003) ATX-1, an Arabidopsis homolog of trithorax, activates flower homeotic genes. Curr Biol 13 627–637 - PubMed
-
- Ben-Yacoub S, Abdeljaoued Y, Mayoraz E (1999) Fusion of face and speech data for person identity verification. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 10 1065–1074 - PubMed
-
- Bhardwaj N, Lu H (2005) Correlation between gene expression profiles and protein-protein interactions within and across genomes. Bioinformatics 21 2730–2738 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

