Insulin therapy to improve BMI in cystic fibrosis-related diabetes without fasting hyperglycemia: results of the cystic fibrosis related diabetes therapy trial
- PMID: 19592632
- PMCID: PMC2752940
- DOI: 10.2337/dc09-0585
Insulin therapy to improve BMI in cystic fibrosis-related diabetes without fasting hyperglycemia: results of the cystic fibrosis related diabetes therapy trial
Abstract
Objective: Cystic fibrosis-related diabetes (CFRD) without fasting hyperglycemia (CFRD FH-) is not associated with microvascular or macrovascular complications, leading to controversy about the need for treatment. The Cystic Fibrosis Related Diabetes Therapy (CFRDT) Trial sought to determine whether diabetes therapy improves BMI in these patients.
Research design and methods: A three-arm multicenter randomized trial compared 1 year of therapy with premeal insulin aspart, repaglinide, or oral placebo in subjects with cystic fibrosis who had abnormal glucose tolerance.
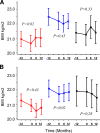
Results: One hundred adult patients were enrolled. Eighty-one completed the study, including 61 with CFRD FH- and 20 with severly impaired glucose tolerance (IGT). During the year before therapy, BMI declined in all groups. Among the group with CFRD FH-, insulin-treated patients lost 0.30 +/- 0.21 BMI units the year before therapy. After 1 year of insulin therapy, this pattern reversed, and they gained 0.39 +/- 21 BMI units (P = 0.02). No significant change in the rate of BMI decline was seen in placebo-treated patients (P = 0.45). Repaglinide-treated patients had an initial significant BMI gain (0.53 +/- 0.19 BMI units, P = 0.01), but this effect was not sustained. After 6 months of therapy they lost weight so that by 12 months there was no difference in the rate of BMI change during the study year compared with the year before (P = 0.33). Among patients with IGT, neither insulin nor repaglinide affected the rate of BMI decline. No significant differences were seen in the rate of lung function decline or the number of hospitalizations in any group.
Conclusions: Insulin therapy safely reversed chronic weight loss in patients with CFRD FH-.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00072904.
Figures
References
-
- Moran A, Doherty L, Wang X, Thomas W: Abnormal glucose metabolism in cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr 1998;133:10–16 - PubMed
-
- Moran A, Hardin D, Rodman D, Allen HF, Beall RJ, Borowitz D, Brunzell C, Campbell PW, Chesrown SE, Duchow C, Fink RJ, FitzSimmons SC, Hamilton N, Hirsch I, Howenstine MS, Klein DJ, Madhun Z, Pencharz PB, Quittner AL, Robbins MK, Schindler T, Schissel K, Schwarzenberg SJ, Stallings VA, Tullis DE, Zipf WB: Diagnosis, screening, and management of CFRD: a consensus conference report. J Diabetes Res Clin Pract 1999;45:55–71 - PubMed
-
- Schwarzenberg SJ, Thomas W, Olsen TW, Grover T, Walk D, Milla CE, Moran A: Microvascular complications in cystic fibrosis-related diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007;30:1056–1061 - PubMed
-
- Moran A, Milla C, DuCret R, Nair KS: Protein metabolism in clinically stable adult CF patients with abnormal glucose tolerance. Diabetes 2001;50:1336–1343 - PubMed
-
- Moran A, Basu R, Milla C, Jensen M: Insulin regulation of free fatty acid kinetics in adult cystic fibrosis patients with impaired glucose tolerance. Metabolism 2004;53:1467–1472 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

