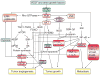
PI3K/PTEN signaling in angiogenesis and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 19595306
- PMCID: PMC2933405
- DOI: 10.1016/S0065-230X(09)02002-8
PI3K/PTEN signaling in angiogenesis and tumorigenesis
Abstract
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) and phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) signaling pathway play an important role in multiple cellular functions such as cell metabolism, proliferation, cell-cycle progression, and survival. PI3K is activated by growth factors and angiogenesis inducers such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and angiopoietins. The amplification and mutations of PI3K and the loss of the tumor suppressor PTEN are common in various kinds of human solid tumors. The genetic alterations of upstream and downstream of PI3K signaling molecules such as receptor tyrosine kinases and AKT, respectively, are also frequently altered in human cancer. PI3K signaling regulates tumor growth and angiogenesis by activating AKT and other targets, and by inducing HIF-1 and VEGF expression. Angiogenesis is required for tumor growth and metastasis. In this review, we highlight the recent studies on the roles and mechanisms of PI3K and PTEN in regulating tumorigenesis and angiogenesis, and the roles of the downstream targets of PI3K for transmitting the signals. We also discuss the crosstalk of these signaling molecules and cellular events during tumor growth, metastasis, and tumor angiogenesis. Finally, we summarize the potential applications of PI3K, AKT, and mTOR inhibitors and their outcome in clinical trials for cancer treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PTEN regulates angiogenesis through PI3K/Akt/VEGF signaling pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2009 Nov;331(1-2):161-71. doi: 10.1007/s11010-009-0154-x. Epub 2009 May 13. Mol Cell Biochem. 2009. PMID: 19437103
-
PI3K/PTEN/AKT signaling regulates prostate tumor angiogenesis.Cell Signal. 2007 Dec;19(12):2487-97. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2007.07.025. Epub 2007 Aug 15. Cell Signal. 2007. PMID: 17826033 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/PTEN signaling in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jan;1784(1):150-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2007.09.008. Epub 2007 Sep 29. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 17964232 Review.
-
Repression of microRNA-21 inhibits retinal vascular endothelial cell growth and angiogenesis via PTEN dependent-PI3K/Akt/VEGF signaling pathway in diabetic retinopathy.Exp Eye Res. 2020 Jan;190:107886. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2019.107886. Epub 2019 Nov 21. Exp Eye Res. 2020. PMID: 31759996
-
The PTEN⁻PI3K Axis in Cancer.Biomolecules. 2019 Apr 17;9(4):153. doi: 10.3390/biom9040153. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 30999672 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism rs17849071 G/T in the PIK3CA gene is inversely associated with follicular thyroid cancer and PIK3CA amplification.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49192. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049192. Epub 2012 Nov 21. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23185308 Free PMC article.
-
Rapamycin-Loaded Lipid Nanocapsules Induce Selective Inhibition of the mTORC1-Signaling Pathway in Glioblastoma Cells.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Feb 25;8:602998. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.602998. eCollection 2020. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33718332 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of extended RAS and PIK3CA gene mutation status with outcomes from the phase III AGITG MAX STUDY involving capecitabine alone or in combination with bevacizumab plus or minus mitomycin C in advanced colorectal cancer.Br J Cancer. 2015 Mar 17;112(6):963-70. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.37. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25742472 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
AKTivation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway by KSHV.Front Immunol. 2013 Jan 7;3:401. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2012.00401. eCollection 2012. Front Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23316192 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis of the cerebral hippocampal tissue in spontaneously hypertensive rats exposed to acute hypobaric hypoxia: associations with inflammation and energy metabolism.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 6;13(1):3681. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30682-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36878975 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Agarwal A, Das K, Lerner N, Sathe S, Cicek M, Casey G, Sizemore N. The AKT/I kappa B kinase pathway promotes angiogenic/metastatic gene expression in colorectal cancer by activating nuclear factor-kappa B and beta-catenin. Oncogene. 2005;24:1021–1031. - PubMed
-
- Argiris A, Cohen E, Karrison T, Esparaz B, Mauer A, Ansari R, Wong S, Lu Y, Pins M, Dancey J, Vokes E. A phase II trial of perifosine, an oral alkylphospholipid, in recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2006;5:766–770. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous