A structural view on the mechanism of the ribosome-catalyzed peptide bond formation
- PMID: 19595805
- PMCID: PMC2783306
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2009.06.006
A structural view on the mechanism of the ribosome-catalyzed peptide bond formation
Abstract
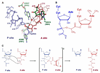
The ribosome is a large ribonucleoprotein particle that translates genetic information encoded in mRNA into specific proteins. Its highly conserved active site, the peptidyl-transferase center (PTC), is located on the large (50S) ribosomal subunit and is comprised solely of rRNA, which makes the ribosome the only natural ribozyme with polymerase activity. The last decade witnessed a rapid accumulation of atomic-resolution structural data on both ribosomal subunits as well as on the entire ribosome. This has allowed studies on the mechanism of peptide bond formation at a level of detail that surpasses that for the classical protein enzymes. A current understanding of the mechanism of the ribosome-catalyzed peptide bond formation is the focus of this review. Implications on the mechanism of peptide release are discussed as well.
Figures

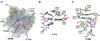




References
-
- Lake JA. Ribosome structure determined by electron microscopy of Escherichia coli small subunits, large subunits and monomeric ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1976;105:131–139. - PubMed
-
- Green R, Noller HF. Ribosomes and translation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1997;66:679–716. - PubMed
-
- Trakhanov SD, Yusupov MM, Agalarov SC, Garver MB, Ryazantsev SN, Tischenko SV, Shirokov VA. Crystallization of 70S ribosomes and 30S ribosomal subunits from Thermus thermophilus. FEBS Lett. 1987;220:319–322.
-
- von Bohlen K, Makowski I, Hansen HA, Bartels H, Berkovitch-Yellin Z, Zaytzev-Bashan A, Meyer S, Paulke C, Franceschi F, Yonath A. Characterization and preliminary attempts for derivatization of crystals of large ribosomal subunits from Haloarcula marismortui diffracting to 3 Å resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991;222:11–15. - PubMed
-
- Yonath A, Mussig J, Tesche B, Lorenz S, Erdmann VA, Wittmann HG. Crystallization of the large ribosomal subunits from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochem. Int. 1980;1:428–435.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

