Biology and treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis
- PMID: 19596009
- PMCID: PMC4104422
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.07.007
Biology and treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis
Abstract
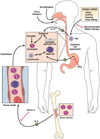
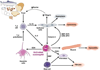
Eosinophilic esophagitis is a recently recognized but expanding disorder characterized by antigen-driven eosinophil accumulation in the esophagus. Symptoms frequently mimic those of gastroesophageal reflux disease, but the diseases are distinct in their histopathology, gene expression signature, response to therapy, hereditary risk, and association with allergies. The pathogenesis of eosinophilic esophagitis involves environmental and genetic factors, particularly food antigens and expression level of the eosinophil chemoattractant eotaxin-3, respectively. Analyses of gene expression signatures and animal models have indicated the importance of adaptive T-cell immunity that involves interleukin-5 and interleukin-13-induced esophageal epithelial cell responses. Symptoms, dysregulation of esophageal gene expression, and pathology are largely reversible following reduced exposure to specific food antigens as well as anti-inflammatory therapy, but chronic treatment is necessary to prevent relapse. Therefore, eosinophilic esophagitis is a disease with unique features that include chronic esophagitis, atopy, immune sensitization to oral antigens, reversibility, and familial association.
Figures

References
-
- Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders (EGID) J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;113:11–28. - PubMed
-
- Balatsinou C, Milano A, Caldarella MP, Laterza F, Pierdomenico SD, Cuccurullo F, Neri M. Eosinophilic esophagitis is a component of the anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome: Description of two cases. Dig Liver Dis. 2007 - PubMed
-
- Noble C, Francis L, Withers GW, Ee LC, Lewindon PJ. Audit of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children post-liver transplant. Pediatr Transplant. 2008 - PubMed
-
- Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, Gupta SK, Justinich C, Putnam PE, Bonis P, Hassall E, Straumann A, Rothenberg ME. Eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adults: a systematic review and consensus recommendations for diagnosis and treatment. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1342–1363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

