Estrogen receptor alpha and beta specific agonists regulate expression of synaptic proteins in rat hippocampus
- PMID: 19596275
- PMCID: PMC2778245
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.06.090
Estrogen receptor alpha and beta specific agonists regulate expression of synaptic proteins in rat hippocampus
Abstract
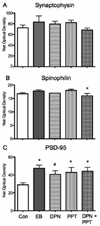
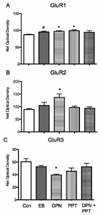
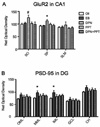
Changes in hippocampal CA1 dendritic spine density and synaptic number across the estrous cycle in female rats correlate with increased hippocampal-dependent cognitive performance in a manner that is dependent on estrogen receptors (ERs). Two isoforms of the estrogen receptor, alpha and beta are present in the rat hippocampus and distinct effects on cognitive behavior have been described for each receptor. The present study generated a profile of synaptic proteins altered by administration of estradiol benzoate, the ERalpha selective agonist PPT (1,3,5-tris (4-hydroxyphenyl)-4-propyl-1H-pyrazole) and the ERbeta selective agonist DPN (2,3-bis (4-hydroxyphenyl) propionitrile) alone and in combination in comparison to vehicle in the CA1 region of the dorsal hippocampus. In the stratum radiatum, estradiol, DPN, and PPT increased PSD-95 and AMPA-type glutamate receptor subunit GluR1. Only DPN administration regulated expression of AMPA receptor subunits GluR2 and GluR3, increasing and decreasing levels respectively. DPN also increased GluR2 expression in the other lamina of the CA1. These results support previous reports that estradiol and isoform specific agonists differentially activate ERalpha and ERbeta to regulate protein expression. The distinct effects of DPN and PPT administration on synaptic proteins suggest that the desired therapeutic outcome of estrogen may be accomplished by using specific estrogen receptor agonists. Moreover, the effects of estradiol treatment on PSD-95 expression are consistent with a growing body of evidence that this postsynaptic protein is a key marker of estrogen action related to spine synapse formation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Contribution of estrogen receptor subtypes, ERα, ERβ, and GPER1 in rapid estradiol-mediated enhancement of hippocampal synaptic transmission in mice.Hippocampus. 2015 Dec;25(12):1556-66. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22475. Epub 2015 Jun 12. Hippocampus. 2015. PMID: 25980457 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of oestrogen receptor alpha and beta agonists on brain N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors.J Neuroendocrinol. 2008 Aug;20(8):1006-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2008.01754.x. Epub 2008 May 27. J Neuroendocrinol. 2008. PMID: 18510708
-
Estradiol targets synaptic proteins to induce glutamatergic synapse formation in cultured hippocampal neurons: critical role of estrogen receptor-alpha.J Neurosci. 2007 Jun 27;27(26):6903-13. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0909-07.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17596438 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid modulation of synaptic plasticity by estrogens as well as endocrine disrupters in hippocampal neurons.Brain Res Rev. 2008 Mar;57(2):363-75. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2007.06.010. Epub 2007 Jul 28. Brain Res Rev. 2008. PMID: 17822775 Review.
-
Contribution of estrogen receptors alpha and beta to the effects of estradiol in the brain.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008 Feb;108(3-5):327-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2007.09.011. Epub 2007 Sep 7. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 17936613 Review.
Cited by
-
Estradiol acts via estrogen receptors alpha and beta on pathways important for synaptic plasticity in the mouse hippocampal formation.Neuroscience. 2012 Jan 27;202:131-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.11.035. Epub 2011 Nov 23. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22133892 Free PMC article.
-
Female rats are resistant to developing the depressive phenotype induced by maternal separation stress.Metab Brain Dis. 2016 Feb;31(1):109-19. doi: 10.1007/s11011-015-9723-8. Epub 2015 Sep 7. Metab Brain Dis. 2016. PMID: 26344502
-
Activation of oestrogen receptor α induces a novel form of LTP at hippocampal temporoammonic-CA1 synapses.Br J Pharmacol. 2020 Feb;177(3):642-655. doi: 10.1111/bph.14880. Epub 2020 Jan 17. Br J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31637699 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen: a master regulator of bioenergetic systems in the brain and body.Front Neuroendocrinol. 2014 Jan;35(1):8-30. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2013.08.001. Epub 2013 Aug 29. Front Neuroendocrinol. 2014. PMID: 23994581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Previous estradiol treatment during midlife maintains transcriptional regulation of memory-related proteins by ERα in the hippocampus in a rat model of menopause.Neurobiol Aging. 2021 Sep;105:365-373. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2021.05.022. Epub 2021 Jun 5. Neurobiol Aging. 2021. PMID: 34198140 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Becker JB, Arnold AP, Berkley KJ, Blaustein JD, Eckel LA, Hampson E, Herman JP, Marts S, Sadee W, Steiner M, Taylor J, Young E. Strategies and methods for research on sex differences in brain and behavior. Endocrinology. 2005;146:1650–1673. - PubMed
-
- Boulland JL, Ferhat L, Tallak Solbu T, Ferrand N, Chaudhry FA, Storm-Mathisen J, Esclapez M. Changes in vesicular transporters for gamma-aminobutyric acid and glutamate reveal vulnerability and reorganization of hippocampal neurons following pilocarpine-induced seizures. J Comp Neurol. 2007;503:466–485. - PubMed
-
- Brake WG, Alves SE, Dunlop JC, Lee SJ, Bulloch K, Allen PB, Greengard P, McEwen BS. Novel target sites for estrogen action in the dorsal hippocampus: an examination of synaptic proteins. Endocrinology. 2001;142:1284–1289. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

