Integration of genetic and genomic methods for identification of genes and gene variants encoding QTLs in the nonhuman primate
- PMID: 19596448
- PMCID: PMC2760456
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2009.06.009
Integration of genetic and genomic methods for identification of genes and gene variants encoding QTLs in the nonhuman primate
Abstract
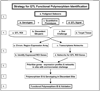
We have developed an integrated approach, using genetic and genomic methods, in conjunction with resources from the Southwest National Primate Research Center (SNPRC) baboon colony, for the identification of genes and their functional variants that encode quantitative trait loci (QTL). In addition, we use comparative genomic methods to overcome the paucity of baboon specific reagents and to augment translation of our findings in a nonhuman primate (NHP) to the human population. We are using the baboon as a model to study the genetics of cardiovascular disease (CVD). A key step for understanding gene-environment interactions in cardiovascular disease is the identification of genes and gene variants that influence CVD phenotypes. We have developed a sequential methodology that takes advantage of the SNPRC pedigreed baboon colony, the annotated human genome, and current genomic and bioinformatic tools. The process of functional polymorphism identification for genes encoding QTLs involves comparison of expression profiles for genes and predicted genes in the genomic region of the QTL for individuals discordant for the phenotypic trait mapping to the QTL. After comparison, genes of interest are prioritized, and functional polymorphisms are identified in candidate genes by genotyping and quantitative trait nucleotide analysis. This approach reduces the time and labor necessary to prioritize and identify genes and their polymorphisms influencing variation in a quantitative trait compared with traditional positional cloning methods.
Figures
References
-
- Cox LA, Birnbaum S, Mahaney MC, Rainwater DL, Williams JT, Vandeberg JL. Circulation. 2007;116:1185–1195. - PubMed
-
- Kammerer C, Cox L, Mahaney M, Rogers J, Shade R. Hypertension. 2001;37:398–402. - PubMed
-
- Kammerer CM, Rainwater DL, Schneider JL, Cox LA, Mahaney MC, Rogers J, Vandeberg JF. Hypertension. 2003;41:854–859. - PubMed
-
- Rainwater DL, Kammerer CM, Mahaney MC, Rogers J, Cox LA, Schneider JL, Vandeberg JL. Atherosclerosis. 2003;168:15–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources