In vivo characterization of the peptide deformylase inhibitor LBM415 in murine infection models
- PMID: 19596876
- PMCID: PMC2737836
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00026-09
In vivo characterization of the peptide deformylase inhibitor LBM415 in murine infection models
Abstract
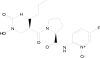
LBM415 is an antibacterial agent belonging to the peptide deformylase inhibitor class of compounds. It has previously been shown to demonstrate good activity in vitro against a range of pathogens. In this study, the in vivo efficacy of LBM415 was evaluated in various mouse infection models. We investigated activity against a systemic infection model caused by intraperitoneal inoculation of Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin [meticillin] susceptible [MSSA] and methicillin resistant [MRSA]) and Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin susceptible [PSSP] and multidrug resistant [MDRSP]), a thigh infection model caused by intramuscular injection of MRSA, and a lung infection produced by intranasal inoculation of PSSP. In the systemic MSSA and MRSA infections, LBM415 was equivalent to linezolid and vancomycin. In the systemic PSSP infection, LBM415 was equivalent to linezolid, whereas against systemic MDRSP infection, the LBM415 50% effective dose (ED50) was 4.8 mg/kg (dosed subcutaneously) and 36.6 mg/kg (dosed orally), compared to 13.2 mg/kg for telithromycin and >60 mg/kg for penicillin V and clarithromycin. In the MRSA thigh infection, LBM415 significantly reduced thigh bacterial levels compared to those of untreated mice, with levels similar to those after treatment with linezolid at the same dose levels. In the pneumonia model, the ED50 to reduce the bacterial lung burden by >4 log10 in 50% of treated animals was 23.3 mg/kg for LBM415, whereas moxifloxacin showed an ED50 of 14.3 mg/kg. In summary, LBM415 showed in vivo efficacy in sepsis and specific organ infection models irrespective of resistance to other antibiotics. Results suggest the potential of peptide deformylase inhibitors as a novel class of therapeutic agents against antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
Figures
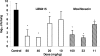
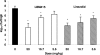
Similar articles
-
In vivo pharmacodynamics of a new oxazolidinone (linezolid).Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002 Nov;46(11):3484-9. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.11.3484-3489.2002. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002. PMID: 12384354 Free PMC article.
-
Antistaphylococcal activity of LBM415, a new peptide deformylase inhibitor, compared with those of other agents.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004 Oct;48(10):4033-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.48.10.4033-4036.2004. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15388473 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial activity of a novel peptide deformylase inhibitor, LBM415, tested against respiratory tract and cutaneous infection pathogens: a global surveillance report (2003-2004).J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006 May;57(5):914-23. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl093. Epub 2006 Mar 20. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16549511
-
[Therapeutic perspectives of linezolid in the management of infections due to multiresistant Gram-positive pathogens].Recenti Prog Med. 2007 Mar;98(3):143-54. Recenti Prog Med. 2007. PMID: 17484159 Review. Italian.
-
[Linezolid--novel antibiotic for the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections].Wiad Lek. 2006;59(9-10):727-31. Wiad Lek. 2006. PMID: 17338140 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Advances in MRSA drug discovery: where are we and where do we need to be?Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2013 Sep;8(9):1095-116. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2013.807246. Epub 2013 Jul 6. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23829425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ligand and Structure-Based Approaches for the Identification of Peptide Deformylase Inhibitors as Antibacterial Drugs.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 15;17(7):1141. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071141. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27428963 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Pharmacokinetics of IDP-73152 in Humans Using Physiologically-Based Pharmacokinetics.Pharmaceutics. 2022 May 28;14(6):1157. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14061157. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35745730 Free PMC article.
-
Fighting Antimicrobial Resistance: Innovative Drugs in Antibacterial Research.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 Mar 3;64(10):e202414325. doi: 10.1002/anie.202414325. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 39611429 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potent sub-MIC effect of GSK1322322 and other peptide deformylase inhibitors on in vitro growth of Staphylococcus aureus.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(1):290-6. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01292-13. Epub 2013 Oct 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24165188 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brown, S. D., and D. J. Farrell. 2004. Antibacterial susceptibility among Streptococcus pneumoniae isolated from paediatric and adult patients as part of the PROTEKT US study in 2001-2002. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 54:i23-i29. - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. 2006. Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically. Approved standard—7th ed. CLSI document M7-A7. CLSI, Wayne, PA.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

