Epistatic effects of the protease/chaperone HflB on some damaged forms of the Escherichia coli ammonium channel AmtB
- PMID: 19596908
- PMCID: PMC2787424
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.109.103747
Epistatic effects of the protease/chaperone HflB on some damaged forms of the Escherichia coli ammonium channel AmtB
Abstract
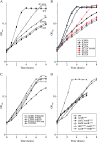
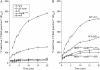
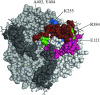
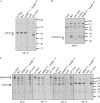
The Escherichia coli ammonium channel AmtB is a trimer in which each monomer carries a pore for substrate conduction and a cytoplasmic C-terminal extension of approximately 25 residues. Deletion of the entire extension leaves the protein with intermediate activity, but some smaller lesions in this region completely inactivate AmtB, as do some lesions in its cytoplasmic loops. We here provide genetic evidence that inactivation depends on the essential protease HflB, which appears to cause inactivation not as a protease but as a chaperone. Selection for restored function of AmtB is a positive selection for loss of the ATPase/chaperone activity of HflB and reveals that the conditional lethal phenotype for hflB is cold sensitivity. Deletion of only a few residues from the C terminus of damaged AmtB proteins seems to prevent HflB from acting on them. Either yields the intermediate activity of a complete C-terminal deletion. HflB apparently "tacks" damaged AmtB tails to the adjacent monomers. Knowing that HflB has intervened is prerequisite to determining the functional basis for AmtB inactivation.
Figures



References
-
- Akiyama, Y., A. Kihara, H. Tokuda and K. Ito, 1996. FtsH (HflB) is an ATP-dependent protease selectively acting on SecY and some other membrane proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 271 31196–31201. - PubMed
-
- Andrade, S. L., and O. Einsle, 2007. The Amt/Mep/Rh family of ammonium transport proteins. Mol. Membr. Biol. 24 357–365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

