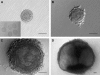
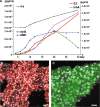
In vitro grown human ovarian follicles from cancer patients support oocyte growth
- PMID: 19597190
- PMCID: PMC2743446
- DOI: 10.1093/humrep/dep228
In vitro grown human ovarian follicles from cancer patients support oocyte growth
Abstract
Background: Young female adult and adolescent cancer patients facing life-preserving but fertility-threatening chemo- or radiation-therapy are increasingly seeking options to protect their reproductive potential. Ovarian tissue cryopreservation with transplantation is a promising technique to safeguard fertility in cancer patients. However, this method may risk re-introduction of the original cancer to the survivor of the disease. Thus, developing a method for in vitro growth of immature follicles may provide a method for fertility restoration in the future.
Methods: Human secondary follicles were isolated from ovarian tissues obtained from cancer patients and grown in vitro within a bio-engineered culture system for 30 days.
Results: Human ovarian follicles became steroidogenically active, and developed from the early secondary to antral stage in vitro. The follicles contained healthy, growing oocytes that were connected by transzonal projections between the somatic cells and oocyte.
Conclusions: Our data support the notion that human follicle development can be achieved in vitro in a bio-engineered culture system. More studies are required to investigate whether the fully sized oocytes obtained from in vitro grown follicle are competent to resume meiosis and be fertilized.
Figures
References
-
- Abir R, Franks S, Mobberley MA, Moore PA, Margara RA, Winston RM. Mechanical isolation and in vitro growth of preantral and small antral human follicles. Fertil steril. 1997;68:682–688. - PubMed
-
- Abir R, Roizman P, Fisch B, Nitke S, Okon E, Orvieto R, Ben Rafael Z. Pilot study of isolated early human follicles cultured in collagen gels for 24 hours. Hum Reprod. 1999;14:1299–1301. - PubMed
-
- Abir R, Fisch B, Nitke S, Okon E, Raz A, Ben Rafael Z. Morphological study of fully and partially isolated early human follicles. Fertil Steril. 2001;75:141–146. - PubMed
-
- Abir R, Nitke S, Ben-Haroush A, Fisch B. In vitro maturation of human primordial ovarian follicles: clinical significance, progress in mammals, and methods for growth evaluation. Histol Histopathol. 2006;21:887–898. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal SK, Chang RJ. Fertility management for women with cancer. Cancer Treat Res. 2007;138:15–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources