Diversity of chemical mechanisms in thioredoxin catalysis revealed by single-molecule force spectroscopy
- PMID: 19597482
- PMCID: PMC2745927
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.1627
Diversity of chemical mechanisms in thioredoxin catalysis revealed by single-molecule force spectroscopy
Erratum in
- Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009 Dec;16(12):1331. Gaucher, Eric [corrected to Gaucher, Eric A]
Abstract
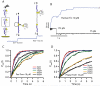
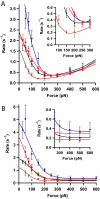
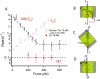
Thioredoxins (Trxs) are oxidoreductase enzymes, present in all organisms, that catalyze the reduction of disulfide bonds in proteins. By applying a calibrated force to a substrate disulfide, the chemical mechanisms of Trx catalysis can be examined in detail at the single-molecule level. Here we use single-molecule force-clamp spectroscopy to explore the chemical evolution of Trx catalysis by probing the chemistry of eight different Trx enzymes. All Trxs show a characteristic Michaelis-Menten mechanism that is detected when the disulfide bond is stretched at low forces, but at high forces, two different chemical behaviors distinguish bacterial-origin from eukaryotic-origin Trxs. Eukaryotic-origin Trxs reduce disulfide bonds through a single-electron transfer reaction (SET), whereas bacterial-origin Trxs show both nucleophilic substitution (S(N)2) and SET reactions. A computational analysis of Trx structures identifies the evolution of the binding groove as an important factor controlling the chemistry of Trx catalysis.
Figures
References
-
- Kraut DA, Carroll KS, Herschlag D. Challenges in enzyme mechanism and energetics. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:517–71. - PubMed
-
- Henzler-Wildman KA, et al. Intrinsic motions along an enzymatic reaction trajectory. Nature. 2007;450:838–44. - PubMed
-
- Dai S, Friemann R, Glauser DA, Bourquin F, Manieri W, Schurmann P, Eklund H. Structural snapshots along the reaction pathway of ferredoxinthioredoxin reductase. Nature. 2007;448:92–6. - PubMed
-
- Mori T, Vale RD, Tomishige M. How kinesin waits between steps. Nature. 2007;450:750–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

