Sex differences in the Toll-like receptor-mediated response of plasmacytoid dendritic cells to HIV-1
- PMID: 19597505
- PMCID: PMC2821111
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.2004
Sex differences in the Toll-like receptor-mediated response of plasmacytoid dendritic cells to HIV-1
Abstract
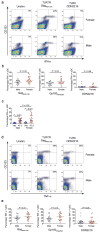
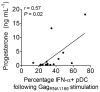
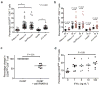
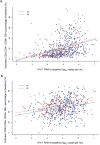
Manifestations of viral infections can differ between women and men, and marked sex differences have been described in the course of HIV-1 disease. HIV-1-infected women tend to have lower viral loads early in HIV-1 infection but progress faster to AIDS for a given viral load than men. Here we show substantial sex differences in the response of plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) to HIV-1. pDCs derived from women produce markedly more interferon-alpha (IFN-alpha) in response to HIV-1-encoded Toll-like receptor 7 (TLR7) ligands than pDCs derived from men, resulting in stronger secondary activation of CD8(+) T cells. In line with these in vitro studies, treatment-naive women chronically infected with HIV-1 had considerably higher levels of CD8(+) T cell activation than men after adjusting for viral load. These data show that sex differences in TLR-mediated activation of pDCs may account for higher immune activation in women compared to men at a given HIV-1 viral load and provide a mechanism by which the same level of viral replication might result in faster HIV-1 disease progression in women compared to men. Modulation of the TLR7 pathway in pDCs may therefore represent a new approach to reduce HIV-1-associated pathology.
Figures
Comment in
-
HIV gender clues emerge.Nat Med. 2009 Aug;15(8):830. doi: 10.1038/nm0809-830b. Nat Med. 2009. PMID: 19661976 No abstract available.
-
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells, Janus-faced sentinels: progesterone, guilty or innocent?Immunotherapy. 2009 Nov;1(6):929-31. doi: 10.2217/imt.09.71. Immunotherapy. 2009. PMID: 20635911
References
-
- Katzenstein DA, et al. The relation of virologic and immunologic markers to clinical outcomes after nucleoside therapy in HIV-infected adults with 200 to 500 CD4 cells per cubic millimeter. AIDS Clinical Trials Group Study 175 Virology Study Team. N Engl J Med. 1996;335:1091–8. - PubMed
-
- Farzadegan H, et al. Sex differences in HIV-1 viral load and progression to AIDS. Lancet. 1998;352:1510–4. - PubMed
-
- Evans JS, et al. Serum levels of virus burden in early-stage human immunodeficiency virus type 1 disease in women. J Infect Dis. 1997;175:795–800. - PubMed
-
- Sterling TR, et al. Sex differences in longitudinal human immunodeficiency virus type 1 RNA levels among seroconverters. J Infect Dis. 1999;180:666–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R21 AI071806/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI25879/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI074415/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01AI062435/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027666/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI27659/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027659/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AI062435/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI27666/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI38858/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI038855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001C/RC/CCR NIH HHS/United States
- AI38855/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN261200800001E/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI025879/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

