The role of anorexia in resistance and tolerance to infections in Drosophila
- PMID: 19597539
- PMCID: PMC2701602
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000150
The role of anorexia in resistance and tolerance to infections in Drosophila
Abstract
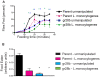
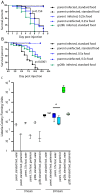
Most infections induce anorexia but its function, if any, remains unclear. Because this response is common among animals, we hypothesized that infection-induced diet restriction might be an adaptive trait that modulates the host's ability to fight infection. Two defense strategies protect hosts against infections: resistance, which is the ability to control pathogen levels, and tolerance, which helps the host endure infection-induced pathology. Here we show that infected fruit flies become anorexic and that diet restriction alters defenses, increasing the fly's tolerance to Salmonella typhimurium infections while decreasing resistance to Listeria monocytogenes. This suggests that attempts to extend lifespan through diet restriction or the manipulation of pathways mimicking this process will have complicated effects on a host's ability to fight infections.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

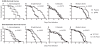

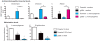
References
-
- Hart BL. Biological basis of behavior of sick animals. Neurosci Behav Rev. 1988;12:123–137. - PubMed
-
- Kyriazakis I, Tolkamp BJ, Hutchings MR. Towards a functional explanation for the occurrence of anorexia during parasitic infections. Anim Behav. 1998;52:265–274. - PubMed
-
- Exton MS. Infection-induced anorexia: active host defense strategy. Appetite. 1997;29:369–383. - PubMed
-
- Dunn PE, Bohnert TJ, Rusell V. Regulation of antimicrobial protein synthesis following infection and during metamorphosis of Manduca sexta. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994;712:117–130. - PubMed
-
- Adamo SA. Parasitic suppression of feeding in the tobacco hornworm,Manduca sexta: parallels with feeding depression after an immune challenge. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol. 2005;60:185–197. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

