TAT peptide and its conjugates: proteolytic stability
- PMID: 19601640
- PMCID: PMC2889171
- DOI: 10.1021/bc900081e
TAT peptide and its conjugates: proteolytic stability
Abstract
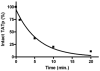
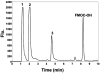
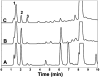
The proteolytic cleavage of TATp, TATp-PEG(1000)-PE conjugate (TATp-conjugate), and TATp as TATp-conjugate in mixed micelles made of TATp-conjugate and PEG(5000)-PE (2.5% mol of TATp-conjugate, TATp-Mic) were studied by HPLC with fluorescent detection using fluorenylmethyl chloroformate (FMOC) labeling and by MALDI-TOF MS analysis. The cleavage kinetics were analyzed in human blood plasma and in trypsin-containing phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.4, to simulate the proteolytic activity of human plasma. The trypsinolysis of free TATp, TATp-conjugate, and TATp-Mic revealed that the main initial fragmentation is an endocleavage at the carboxyl terminus resulting in an Arg-Arg (RR) dimer. The trypsinolysis followed pseudo-first-order kinetics. The cleavage of the free TATp was relatively fast with a half-life of a few minutes (t(1/2) ∼ 3.5 min). The TATp-conjugate showed more stability with about a 3-fold increase in half-life (t(1/2) ∼ 10 min). TATp in TATp-Mic was highly protected against proteolysis with an over 100-fold increase in half-life (t(1/2) ∼ 430 min). The shielding of TATp by PEG moieties in the proposed TATp-Mic is of great importance for its potential use as a cell-penetrating moiety for multifunctional "smart" drug delivery systems with detachable PEG.
Figures







References
-
- Frankel AD, Pabo CO. Cellular uptake of the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell. 1988;55:1189–1193. - PubMed
-
- Schwarze SR, Ho A, Vocero-Akbani A, Dowdy SF. In vivo protein transduction: delivery of a biologically active protein into the mouse. Science. 1999;285:1569–1572. - PubMed
-
- Ryser HJ, Hancock R. Histones and basic polyamino acids stimulate the uptake of albumin by tumor cells in culture. Science. 1965;150:501–503. - PubMed
-
- Goun EA, Pillow TH, Jones LR, Rothbard JB, Wender PA. Molecular transporters: synthesis of oligoguanidinium transporters and their application to drug delivery and real-time imaging. Chem Bio Chem. 2006;7:1497–1515. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

