The roles of antimicrobial peptides in innate host defense
- PMID: 19601838
- PMCID: PMC2750833
- DOI: 10.2174/138161209788682325
The roles of antimicrobial peptides in innate host defense
Abstract
Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are multi-functional peptides whose fundamental biological role in vivo has been proposed to be the elimination of pathogenic microorganisms, including Gram-positive and -negative bacteria, fungi, and viruses. Genes encoding these peptides are expressed in a variety of cells in the host, including circulating phagocytic cells and mucosal epithelial cells, demonstrating a wide range of utility in the innate immune system. Expression of these genes is tightly regulated; they are induced by pathogens and cytokines as part of the host defense response, and they can be suppressed by bacterial virulence factors and environmental factors which can lead to increased susceptibility to infection. New research has also cast light on alternative functionalities, including immunomodulatory activities, which are related to their unique structural characteristics. These peptides represent not only an important component of innate host defense against microbial colonization and a link between innate and adaptive immunity, but also form a foundation for the development of new therapeutic agents.
Figures
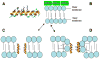
References
-
- Brogden KA. Antimicrobial peptides: pore formers or metabolic inhibitors in bacteria? Nat Rev Microbiol. 2005;3:238–50. - PubMed
-
- Diamond G, Laube D, Klein-Patel ME. In: Mammalian Host Defence Peptides. Hancock REW, Devine DA, editors. Vol. 6. Cambridge University Press; UK: Cambridge: 2004. pp. 111–38.
-
- Hancock REW, Diamond G. The role of cationic antimicrobial peptides in innate host defences. Trends Microbiol. 2000;8:402–10. - PubMed
-
- Kaiser V, Diamond G. Expression of mammalian defensin genes. J Leukoc Biol. 2000;68:779–84. - PubMed
-
- Yeaman MR, Yount NY. Mechanisms of antimicrobial peptide action and resistance. Pharmacol Rev. 2003;55:27–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DE17334/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE015510/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI52316/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01DE14897/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01DE15510/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE018276/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DE018781/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE16334/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL67871/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE18276/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067871/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE017334/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE014897/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE016334/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

