The missing link between indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase mediated antibacterial and immunoregulatory effects
- PMID: 19602041
- PMCID: PMC4496108
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2008.00542.x
The missing link between indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase mediated antibacterial and immunoregulatory effects
Abstract
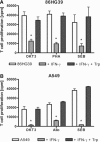
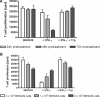
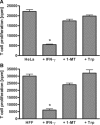
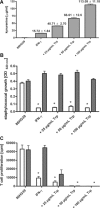
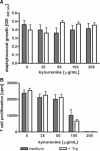
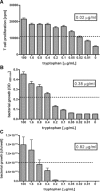
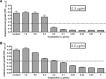
The interferon (IFN)-gamma-inducible tryptophan degrading enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) has not only been recognized as a potent antimicrobial effector molecule for the last 25 years but was recently found also to have potent immunoregulatory properties. In this study, we provide evidence that both tryptophan starvation and production of toxic tryptophan metabolites are involved in the immunoregulation mediated by IDO, whereas tryptophan starvation seems to be the only antibacterial effector mechanism. A long-studied controversy in the IDO research field is the seemingly contradictory effect of IDO in the defence against infectious diseases. On the one hand, IFN-gamma-induced IDO activity mediates an antimicrobial effect, while at the same time IDO inhibits T-cell proliferation and IFN-gamma production. Here, we suggest that both effects, dependent on the threshold for tryptophan, cooperate in a reasonable coherence. We found that the minimum concentration of tryptophan required for bacterial growth is 10-40-fold higher than the minimum concentration necessary for T-cell activation. Therefore, we suggest that during the first phase of infection the IDO-mediated tryptophan depletion has a predominantly antimicrobial effect whereas in the next stage, and with ongoing tryptophan degradation, the minimum threshold concentration of tryptophan for T-cell activation is undercut, resulting in an inhibition of T-cell growth and subsequent IDO activation.
Figures
References
-
- Mellor AL, Munn DH. Creating immune privilege: active local suppression that benefits friends, but protects foes. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:74–80. - PubMed
-
- Steinman RM, Hawiger D, Nussenzweig MC. Tolerogenic dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21:685–711. - PubMed
-
- Munn DH, Zhou M, Attwood JT, Bondarev I, Conway SJ, Marshall B, Brown C, Mellor AL. Prevention of allogeneic fetal rejection by tryptophan catabolism. Science. 1998;281:1191–3. - PubMed
-
- Munn DH, Sharma MD, Lee JR, Jhaver KG, Johnson TS, Keskin DB, Marshall B, Chandler P, Antonia SJ, Burgess R, Slingluff CL, Jr, Mellor AL. Potential regulatory function of human dendritic cells expressing indoleamine 2,3-dioxy-genase. Science. 2002;297:1867–70. - PubMed
-
- Baban B, Hansen AM, Chandler PR, Manlapat A, Bingaman A, Kahler DJ, Munn DH, Mellor AL. A minor population of splenic dendritic cells expressing CD19 mediates IDO-dependent T cell suppression via type I IFN signaling following B7 ligation. Int Immunol. 2005;17:909–19. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

