Coexpression of invasive markers (uPA, CD44) and multiple drug-resistance proteins (MDR1, MRP2) is correlated with epithelial ovarian cancer progression
- PMID: 19603017
- PMCID: PMC2720231
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605185
Coexpression of invasive markers (uPA, CD44) and multiple drug-resistance proteins (MDR1, MRP2) is correlated with epithelial ovarian cancer progression
Abstract
Background: Invasion and metastases of cancer cells and the development of resistance to anticancer therapies are the main causes of treatment failure and mortality in cancer patients.
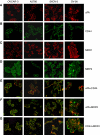
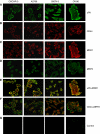
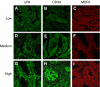
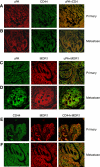
Methods: We evaluated invasive markers of urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA) and CD44 and multiple drug-resistance (MDR) markers of MDR1 and MRP2 in four epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) cell lines, primary tumours (n=120) and matched metastatic lesions (n=40) by immunofluoresence labelling. We correlated uPA and CD44 with MDR markers in primary and metastatic cells using confocal microscope. We also investigated the relationship of the expression of uPA, CD44 and MDR1 with various progression parameters.
Results: The coexpression of uPA and CD44 with MDR markers was found in primary and metastatic cells. The overexpression of uPA, CD44 and MDR1 was found in most primary and matched metastatic lesions of EOC, and was significantly associated with tumour stage, grade, residual disease status, relapse and presence of ascites (P<0.05), but not with histology type (P>0.05).
Conclusions: Our results suggest that the overexpression of uPA, CD44 and MRD1 is correlated with EOC progression; both uPA and CD44 are related with drug resistance during EOC metastasis and could be useful therapeutically.
Figures
References
-
- Afify AM, Craig S, Paulino AF (2006) Temporal variation in the distribution of hyaluronic acid, CD44s, and CD44v6 in the human endometrium across the menstrual cycle. Appl Immunohisto M M 14: 328–333 - PubMed
-
- Andreasen PA, Kjoller L, Christensen L, Duffy MJ (1997) The urokinasetype plasminogen activator system in cancer metastasis: a review. Int J Cancer 72: 1–22 - PubMed
-
- Banzato A, Bobisse S, Rondina M, Renier D, Bettella F, Esposito G, Quintieri L, Melendez-Alafort L, Mazzi U, Zanovello P, Rosato A (2008) A paclitaxel-hyaluronan bioconjugate targeting ovarian cancer affords a potent in vivo therapeutic activity. Clin Cancer Res 14: 3598–3606 - PubMed
-
- Berner HS, Davidson B, Berner A, Risberg B, Kristensen GB, Trope CG, Van de Putte G, Nesland JM (2000) Expression of CD44 in effusions of patients diagnosed with serous ovarian carcinoma: diagnostic and prognostic implications. Clin Exp Metastasis 18: 197–202 - PubMed
-
- Berkenblit A, Matulonis UA, Kroener JF, Dezube BJ, Lam GN, Cuasay LC, Brunner N, Jones TR, Silverman MH, Gold MA (2005) A6, a urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA)-derived peptide in patients with advanced gynecologic cancer: a phase I trial. Gynecol Oncol 99: 50–57 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

