The opposing roles of Wnt-5a in cancer
- PMID: 19603030
- PMCID: PMC2720208
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605174
The opposing roles of Wnt-5a in cancer
Abstract
Wnt-5a is one of the most highly investigated non-canonical Wnts and has been implicated in almost all aspects of non-canonical Wnt signalling. In terms of cancer development, Wnt-5a has, until recently, lived in the shadow of its better-characterised relatives. This was largely because of its apparent inability to transform cells or signal through the canonical beta-catenin pathway that is so important in cancer, particularly colorectal cancer. Recent work in a wide range of human tumours has pointed to a critical role for Wnt-5a in malignant progression, but there is conflicting evidence whether Wnt-5a has a tumour-promoting or -suppressing role. Emerging evidence suggests that the functions of Wnt-5a can be drastically altered depending on the availability of key receptors. Hence, the presence or absence of these receptors may go some way to explain the conflicting role of Wnt-5a in different cancers. This review summarises our current understanding of Wnt-5a and cancer.
Figures
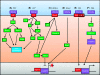
References
-
- Blanc E, Roux GL, Benard J, Raguenez G (2005) Low expression of Wnt-5a gene is associated with high-risk neuroblastoma. Oncogene 24: 1277–1283 - PubMed
-
- Chien AJ, Moore EC, Lonsdorf AS, Kulikauskas RM, Rothberg BG, Berger AJ, Major MB, Hwang ST, Rimm DL, Moon RT (2009) Activated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in melanoma is associated with decreased proliferation in patient tumors and a murine melanoma model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106: 1193–1198 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Da Forno PD, Pringle JH, Hutchinson P, Osborn J, Huang Q, Potter L, Hancox RA, Fletcher A, Saldanha GS (2008) WNT5A expression increases during melanoma progression and correlates with outcome. Clin Cancer Res 14: 5825–5832 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

