Mapping the Micromechanical Properties of Cryo-sectioned Aortic Tissue with Scanning Acoustic Microscopy
- PMID: 19603080
- PMCID: PMC2709223
- DOI: 10.1557/PROC-1132-Z03-07
Mapping the Micromechanical Properties of Cryo-sectioned Aortic Tissue with Scanning Acoustic Microscopy
Abstract
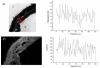
Although the gross mechanical properties of ageing tissues have been extensively documented, biological tissues are highly heterogeneous and little is known concerning the variation of micro-mechanical properties within tissues. Here, we use Scanning Acoustic Microscopy (SAM) to map the acoustic wave speed (a measure of stiffness) as a function of distance from the outer adventitial layer of cryo-sectioned ferret aorta. With a 400 MHz lens, the images of the aorta samples matched those obtained following chemical fixation and staining of sections which were viewed with fluorescence microscopy. Quantitative analysis was conducted with a frequency scanning or V(f) technique by imaging the tissue from 960 MHz to 1.1 GHz. Undulating acoustic wave speed (stiffness) distributions corresponded with elastic fibre locations in the tissue; there was a decrease in wave speed of around 40 ms(-1) from the adventitia (outer layer) to the intima (innermost).
Figures


References
-
- Kielty CM, Sherratt MJ, Shuttleworth CA. J. Cell Sci. 2002;115:2817. - PubMed
-
- Sherratt MJ, Baldock C, Haston JL, Holmes DF, Jones CJP, Shuttleworth CA, Wess TJ, Kielty CM. J. Mol. Bio. 2003;332:183. - PubMed
-
- Lai-Fook SJ, Hyatt RE. J. Appl. Physiol. 2000;89:163. - PubMed
-
- Escoffier C, de Rigal J, Rochefort A, Vasselet R, Leveque JL, Agache PG. The Journal of investigative dermatology. 1989;93:353. - PubMed
-
- Lederle FA. Ann. of Intern. Med. 2003;139:516. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
