INSM1 promoter-driven adenoviral herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase cancer gene therapy for the treatment of primitive neuroectodermal tumors
- PMID: 19604042
- PMCID: PMC2829462
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2008.168
INSM1 promoter-driven adenoviral herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase cancer gene therapy for the treatment of primitive neuroectodermal tumors
Abstract
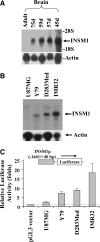
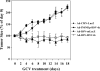
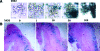
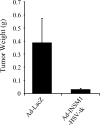
The INSM1 gene encodes a developmentally regulated zinc finger transcription factor. INSM1 expression is normally absent in adult tissues, but is reactivated in neuroendocrine tumor cells. In the present study, we analyzed the therapeutic potential of an adenoviral INSM1 promoter-driven herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase (HSV-tk) construct in primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNETs). We constructed an adenoviral INSM1 promoter-driven HSV-tk gene for therapy in PNETs. The PNET-specific adeno-INSM1 promoter HSV-tk construct was tested both in vitro and in vivo in a nude mouse tumor model. Northern blot analysis and transient transfection of an INSM1 promoter-driven luciferase reporter gene indicated that the INSM1 promoter was active in neuroblastoma (IMR-32), retinoblastoma (Y79), and medulloblastoma (D283 Med) cells, but not in glioblastoma (U-87 MG) cells. After Ad-INSM1p-HSV-tk infection, the levels of HSV-tk protein expression were consistent with INSM1 promoter activities. Furthermore, in vitro multiplicity of infection and ganciclovir (GCV) sensitivity studies indicated that the INSM1 promoter could mediate specific expression of the HSV-tk gene and selective killing of INSM1-positive PNETs. In vivo intratumoral adenoviral delivery demonstrated that the INSM1 promoter could direct HSV-tk gene expression in a nude mouse tumor model and effectively repressed tumor growth in response to GCV treatment. Taken together, our data show that the INSM1 promoter is specific and effective for targeted cancer gene therapy in PNETs.
Figures
References
-
- Adachi Y. Matsubara S. Muramatsu T. Curiel D.T. Reynolds P.N. Midkine promoter-based adenoviral suicide gene therapy to midkine-positive pediatric tumor. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2002;37:588–592. - PubMed
-
- Anderson L.M. Swaminathan S. Zackon I. Tajuddin A.K. Thimmapaya B. Weitzman S.A. Adenovirus-mediated tissue-targeted expression of the HSVtk gene for the treatment of breast cancer. Gene Ther. 1999;6:854–864. - PubMed
-
- Arvidsson Y. Sumantran V. Watt F. Uramoto H. Funa K. Neuroblastoma-specific cytotoxicity mediated by the Mash1-promoter and E. coli purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Pediatr. Blood Cancer. 2005;44:77–84. - PubMed
-
- Berthold F. Hero B. Neuroblastoma: Current drug therapy recommendations as part of the total treatment approach. Drugs. 2000;59:1261–1277. - PubMed
-
- Black M.E. Kokoris M.S. Sabo P. Herpes simplex virus-1 thymidine kinase mutants created by semi-random sequence mutagenesis improve prodrug-mediated tumor cell killing. Cancer Res. 2001;61:3022–3026. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

