Novel DNA binding properties of the Mcm10 protein from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 19605346
- PMCID: PMC2757242
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.033175
Novel DNA binding properties of the Mcm10 protein from Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
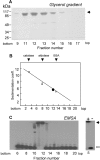
The Mcm10 protein is essential for chromosomal DNA replication in eukaryotic cells. We purified the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mcm10 (ScMcm10) and characterized its DNA binding properties. Electrophoretic mobility shift assays and surface plasmon resonance analysis showed that ScMcm10 binds stably to both double strand (ds) DNA and single strand (ss) DNA. On short DNA templates of 25 or 50 bp, surface plasmon resonance analysis showed a approximately 1:1 stoichiometry of ScMcm10 to dsDNA. On longer dsDNA templates, however, multiple copies of ScMcm10 cooperated in the rapid assembly of a large, stable nucleoprotein complex. The amount of protein bound was directly proportional to the length of the DNA, with an average occupancy spacing of 21-24 bp. This tight spacing is consistent with a nucleoprotein structure in which ScMcm10 is aligned along the helical axis of the dsDNA. In contrast, the stoichiometry of ScMcm10 bound to ssDNA of 20-50 nucleotides was approximately 3:1 suggesting that interaction with ssDNA induces the assembly of a multisubunit ScMcm10 complex composed of at least three subunits. The tight packing of ScMcm10 on dsDNA and the assembly of a multisubunit complex on ssDNA suggests that, in addition to protein-DNA, protein-protein interactions may be involved in forming the nucleoprotein complex. We propose that these DNA binding properties have an important role in (i) initiation of DNA replication and (ii) formation and maintenance of a stable replication fork during the elongation phase of chromosomal DNA replication.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Replication Fork Activation Is Enabled by a Single-Stranded DNA Gate in CMG Helicase.Cell. 2019 Jul 25;178(3):600-611.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.06.032. Cell. 2019. PMID: 31348887 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila MCM10 interacts with members of the prereplication complex and is required for proper chromosome condensation.Mol Biol Cell. 2003 Jun;14(6):2206-15. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e02-11-0706. Epub 2003 Mar 7. Mol Biol Cell. 2003. PMID: 12808023 Free PMC article.
-
Mcm10 regulates the stability and chromatin association of DNA polymerase-alpha.Mol Cell. 2004 Oct 22;16(2):173-85. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2004.09.017. Mol Cell. 2004. PMID: 15494305
-
Enigmatic roles of Mcm10 in DNA replication.Trends Biochem Sci. 2013 Apr;38(4):184-94. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2012.12.003. Epub 2013 Jan 17. Trends Biochem Sci. 2013. PMID: 23332289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fine-tuning of the replisome: Mcm10 regulates fork progression and regression.Cell Cycle. 2019 May;18(10):1047-1055. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2019.1609833. Epub 2019 May 5. Cell Cycle. 2019. PMID: 31014174 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Origin DNA Melting-An Essential Process with Divergent Mechanisms.Genes (Basel). 2017 Jan 11;8(1):26. doi: 10.3390/genes8010026. Genes (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28085061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A critical threshold of MCM10 is required to maintain genome stability during differentiation of induced pluripotent stem cells into natural killer cells.Open Biol. 2024 Jan;14(1):230407. doi: 10.1098/rsob.230407. Epub 2024 Jan 24. Open Biol. 2024. PMID: 38262603 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging players in the initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication.Cell Div. 2012 Oct 17;7(1):22. doi: 10.1186/1747-1028-7-22. Cell Div. 2012. PMID: 23075259 Free PMC article.
-
Mcm10 associates with the loaded DNA helicase at replication origins and defines a novel step in its activation.EMBO J. 2012 May 2;31(9):2195-206. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2012.69. Epub 2012 Mar 20. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22433841 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-parasitic agent suramin and several of its analogues are inhibitors of the DNA binding protein Mcm10.Open Biol. 2019 Aug 30;9(8):190117. doi: 10.1098/rsob.190117. Epub 2019 Aug 14. Open Biol. 2019. PMID: 31409229 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

