Class III phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase alpha and beta are novel host factor regulators of hepatitis C virus replication
- PMID: 19605471
- PMCID: PMC2748049
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02418-08
Class III phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase alpha and beta are novel host factor regulators of hepatitis C virus replication
Abstract
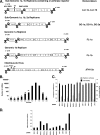
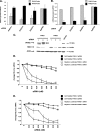
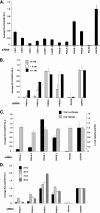
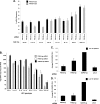
Host factor pathways are known to be essential for hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection and replication in human liver cells. To search for novel host factor proteins required for HCV replication, we screened a subgenomic genotype 1b replicon cell line (Luc-1b) with a kinome and druggable collection of 20,779 siRNAs. We identified and validated several enzymes required for HCV replication, including class III phosphatidylinositol 4-kinases (PI4KA and PI4KB), carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 2, aspartate transcarbamylase, and dihydroorotase (CAD), and mevalonate (diphospho) decarboxylase. Knockdown of PI4KA could inhibit the replication and/or HCV RNA levels of the two subgenomic genotype 1b clones (SG-1b and Luc-1b), two subgenomic genotype 1a clones (SG-1a and Luc-1a), JFH-1 genotype 2a infectious virus (JFH1-2a), and the genomic genotype 1a (FL-1a) replicon. In contrast, PI4KB knockdown inhibited replication and/or HCV RNA levels of Luc-1b, SG-1b, and Luc-1a replicons. The small molecule inhibitor, PIK93, was found to block subgenomic genotype 1b (Luc-1b), subgenomic genotype 1a (Luc-1a), and genomic genotype 2a (JFH1-2a) infectious virus replication in the nanomolar range. PIK93 was characterized by using quantitative chemical proteomics and in vitro biochemical assays to demonstrate PIK93 is a bone fide PI4KA and PI4KB inhibitor. Our data demonstrate that genetic or pharmacological modulation of PI4KA and PI4KB inhibits multiple genotypes of HCV and represents a novel druggable class of therapeutic targets for HCV infection.
Figures

References
-
- Ahn, J., K. Chung, D. Kim, M. Won, L. Kim, K. Kim, M. Nam, S. Choi, H. Kim, M. Yoon, S. Chae, and K. Hoe. 2004. Systematic identification of hepatocellular proteins interacting with NS5A of the hepatitis C virus. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 37:741-748. - PubMed
-
- Aizaki, H., K. Lee, V. Sung, H. Ishiko, and M. Lai. 2004. Characterization of the hepatitis C virus RNA replication complex associated with lipid rafts. Virology 324:450-461. - PubMed
-
- Bader, T., J. Fazili, M. Madhoun, C. Aston, D. Hughes, S. Rizvi, K. Seres, and M. Hasan. 2008. Fluvastatin inhibits hepatitis C replication in humans. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 103:1383-1389. - PubMed
-
- Balla, A., G. Tuymetova, A. Tsiomenko, P. Várnai, and T. Balla. 2005. A plasma membrane pool of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate is generated by phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase type-III alpha: studies with the PH domains of the oxysterol binding protein and FAPP1. Mol. Biol. Cell 16:1282-1295. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

