Use of transdermal melatonin delivery to improve sleep maintenance during daytime
- PMID: 19606092
- PMCID: PMC2909186
- DOI: 10.1038/clpt.2009.109
Use of transdermal melatonin delivery to improve sleep maintenance during daytime
Abstract
Oral melatonin (MEL) can improve daytime sleep, but the hormone's short elimination half-life limits its use as a hypnotic in shift workers and individuals with jet lag or other sleep problems. Here we show, in healthy subjects, that transdermal delivery of MEL during the daytime can elevate plasma MEL and reduce waking after sleep onset, by promoting sleep in the latter part of an 8-h sleep opportunity. Transdermal MEL may have advantages over fast-release oral MEL in improving sleep maintenance during adverse circadian phases.
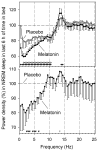
Figures

References
-
- U.S.Congress & Office of Technology Assessment. Biological rhythms: Implications for the worker. U.S. Government Printing Office; Washington, DC: 1991.
-
- Åkerstedt T. Shift work and disturbed sleep/wakefulness. Sleep Med Rev. 1998;2:117–128. - PubMed
-
- Rajaratnam SM, Arendt J. Health in a 24-h society. The Lancet. 2001;358:999–1005. - PubMed
-
- Tzischinsky O, Lavie P. Melatonin possesses time-dependent hypnotic effects. Sleep. 1994;17:638–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

