Curcumin decreased oxidative stress, inhibited NF-kappaB activation, and improved liver pathology in ethanol-induced liver injury in rats
- PMID: 19606259
- PMCID: PMC2709731
- DOI: 10.1155/2009/981963
Curcumin decreased oxidative stress, inhibited NF-kappaB activation, and improved liver pathology in ethanol-induced liver injury in rats
Abstract
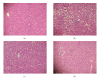
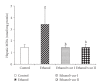
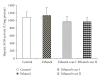
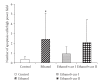
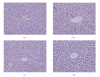
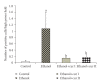
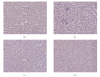
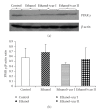
To study the mechanism of curcumin-attenuated inflammation and liver pathology in early stage of alcoholic liver disease, female Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into four groups and treated with ethanol or curcumin via an intragastric tube for 4 weeks. A control group treated with distilled water, and an ethanol group was treated with ethanol (7.5 g/kg bw). Treatment groups were fed with ethanol supplemented with curcumin (400 or 1 200 mg/kg bw). The liver histopathology in ethanol group revealed mild-to-moderate steatosis and mild necroinflammation. Hepatic MDA, hepatocyte apoptosis, and NF-kappaB activation increased significantly in ethanol-treated group when compared with control. Curcumin treatments resulted in improving of liver pathology, decreasing the elevation of hepatic MDA, and inhibition of NF-kappaB activation. The 400 mg/kg bw of curcumin treatment revealed only a trend of decreased hepatocyte apoptosis. However, the results of SOD activity, PPARgamma protein expression showed no difference among the groups. In conclusion, curcumin improved liver histopathology in early stage of ethanol-induced liver injury by reduction of oxidative stress and inhibition of NF-kappaB activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Curcumin prevents alcohol-induced liver disease in rats by inhibiting the expression of NF-kappa B-dependent genes.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003 Feb;284(2):G321-7. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00230.2002. Epub 2002 Aug 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12388178
-
Curcumin Alleviates Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathic Pain through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress-Mediated Activation of NF-κB and Mitigating Inflammation.Biol Pharm Bull. 2020 Feb 1;43(2):348-355. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b19-00862. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Biol Pharm Bull. 2020. PMID: 31776306
-
Curcumin attenuates ethanol-induced hepatic steatosis through modulating Nrf2/FXR signaling in hepatocytes.IUBMB Life. 2015 Aug;67(8):645-58. doi: 10.1002/iub.1409. Epub 2015 Aug 25. IUBMB Life. 2015. PMID: 26305715
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544542. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30580553 Review.
-
Common pathogenic mechanism in development progression of liver injury caused by non-alcoholic or alcoholic steatohepatitis.J Toxicol Sci. 2007 Dec;32(5):453-68. doi: 10.2131/jts.32.453. J Toxicol Sci. 2007. PMID: 18198478 Review.
Cited by
-
Aldose Reductase Inhibitors of Plant Origin in the Prevention and Treatment of Alcoholic Liver Disease: A Minireview.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jun 20;2019:3808594. doi: 10.1155/2019/3808594. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31321234 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of curcumin and exercise rehabilitation on liver paraoxonase-1 and NF-kβ gene expression in the rat induced by forced drinking of ethanol.Clin Exp Hepatol. 2020 Feb;6(1):49-54. doi: 10.5114/ceh.2020.93057. Epub 2020 Feb 17. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 32166124 Free PMC article.
-
Immunohistochemical and molecular study on the protective effect of curcumin against hepatic toxicity induced by paracetamol in Wistar rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Nov 29;14:457. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-457. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25432491 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Oxidative Stress in Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Preclinical Studies.Nutrients. 2024 Apr 15;16(8):1174. doi: 10.3390/nu16081174. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38674865 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated oxidative stress in chronic liver diseases and its mitigation by medicinal plants.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Nov 15;15(11):6321-6341. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 38074830 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tome S, Lucey MR. Review article: current management of alcoholic liver disease. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2004;19(7):707–714. - PubMed
-
- Das SK, Vasudevan DM. Alcohol-induced oxidative stress. Life Sciences. 2007;81(3):177–187. - PubMed
-
- Lieber CS. Pathogenesis and treatment of alcoholic liver disease: progress over the last 50 years. Roczniki Akademii Medycznej w Białymstoku. 2005;50:7–20. - PubMed
-
- Lieber CS. Alcohol and the liver: metabolism of alcohol and its role in hepatic and extrahepatic diseases. Mount Sinai Journal of Medicine. 2000;67(1):84–94. - PubMed
-
- Casey CA, Nanji AA, Cederbaum AI, Adachi M, Takahashi T. Alcoholic liver disease and apoptosis. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research. 2001;25(5):49S–53S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

