OrthoSelect: a protocol for selecting orthologous groups in phylogenomics
- PMID: 19607672
- PMCID: PMC2719630
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-219
OrthoSelect: a protocol for selecting orthologous groups in phylogenomics
Abstract
Background: Phylogenetic studies using expressed sequence tags (EST) are becoming a standard approach to answer evolutionary questions. Such studies are usually based on large sets of newly generated, unannotated, and error-prone EST sequences from different species. A first crucial step in EST-based phylogeny reconstruction is to identify groups of orthologous sequences. From these data sets, appropriate target genes are selected, and redundant sequences are eliminated to obtain suitable sequence sets as input data for tree-reconstruction software. Generating such data sets manually can be very time consuming. Thus, software tools are needed that carry out these steps automatically.
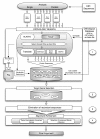
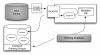
Results: We developed a flexible and user-friendly software pipeline, running on desktop machines or computer clusters, that constructs data sets for phylogenomic analyses. It automatically searches assembled EST sequences against databases of orthologous groups (OG), assigns ESTs to these predefined OGs, translates the sequences into proteins, eliminates redundant sequences assigned to the same OG, creates multiple sequence alignments of identified orthologous sequences and offers the possibility to further process this alignment in a last step by excluding potentially homoplastic sites and selecting sufficiently conserved parts. Our software pipeline can be used as it is, but it can also be adapted by integrating additional external programs. This makes the pipeline useful for non-bioinformaticians as well as to bioinformatic experts. The software pipeline is especially designed for ESTs, but it can also handle protein sequences.
Conclusion: OrthoSelect is a tool that produces orthologous gene alignments from assembled ESTs. Our tests show that OrthoSelect detects orthologs in EST libraries with high accuracy. In the absence of a gold standard for orthology prediction, we compared predictions by OrthoSelect to a manually created and published phylogenomic data set. Our tool was not only able to rebuild the data set with a specificity of 98%, but it detected four percent more orthologous sequences. Furthermore, the results OrthoSelect produces are in absolut agreement with the results of other programs, but our tool offers a significant speedup and additional functionality, e.g. handling of ESTs, computing sequence alignments, and refining them. To our knowledge, there is currently no fully automated and freely available tool for this purpose. Thus, OrthoSelect is a valuable tool for researchers in the field of phylogenomics who deal with large quantities of EST sequences. OrthoSelect is written in Perl and runs on Linux/Mac OS X. The tool can be downloaded at (http://gobics.de/fabian/orthoselect.php).
Figures
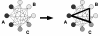


Similar articles
-
OrthoSelect: a web server for selecting orthologous gene alignments from EST sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2009 Jul;37(Web Server issue):W185-8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp434. Epub 2009 Jun 2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009. PMID: 19491309 Free PMC article.
-
JUICE: a data management system that facilitates the analysis of large volumes of information in an EST project workflow.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Nov 23;7:513. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-513. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 17123449 Free PMC article.
-
ESAP plus: a web-based server for EST-SSR marker development.BMC Genomics. 2016 Dec 22;17(Suppl 13):1035. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3328-4. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 28155670 Free PMC article.
-
BIR Pipeline for Preparation of Phylogenomic Data.Evol Bioinform Online. 2015 Apr 27;11:79-83. doi: 10.4137/EBO.S10189. eCollection 2015. Evol Bioinform Online. 2015. PMID: 25987827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Data management in structural genomics: an overview.Methods Mol Biol. 2008;426:49-79. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60327-058-8_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2008. PMID: 18542857 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrating multi-origin expression data improves the resolution of deep phylogeny of ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii).Sci Rep. 2012;2:665. doi: 10.1038/srep00665. Epub 2012 Sep 18. Sci Rep. 2012. PMID: 22993690 Free PMC article.
-
Basal jawed vertebrate phylogenomics using transcriptomic data from Solexa sequencing.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e36256. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036256. Epub 2012 Apr 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22558409 Free PMC article.
-
A novel codon-based de Bruijn graph algorithm for gene construction from unassembled transcriptomes.Genome Biol. 2016 Nov 17;17(1):232. doi: 10.1186/s13059-016-1094-x. Genome Biol. 2016. PMID: 27855707 Free PMC article.
-
Orthograph: a versatile tool for mapping coding nucleotide sequences to clusters of orthologous genes.BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 Feb 16;18(1):111. doi: 10.1186/s12859-017-1529-8. BMC Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28209129 Free PMC article.
-
Insect phylogenomics: exploring the source of incongruence using new transcriptomic data.Genome Biol Evol. 2012;4(12):1295-309. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evs104. Genome Biol Evol. 2012. PMID: 23175716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eisen JA. Phylogenomics: Improving functional predictions for uncharacterized genes by evolutionary analysis. Genome Res. 1998;8:163–167. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

