Patterns of survival and causes of death following a diagnosis of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance: a population-based study
- PMID: 19608666
- PMCID: PMC2791946
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2009.010066
Patterns of survival and causes of death following a diagnosis of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance: a population-based study
Abstract
Background: There are limited data on survival patterns among patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance.
Design and methods: We compared the survival of 4,259 patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, collected from hematology outpatient units in Sweden, with the survival of the general population by computing relative survival ratios. We also compared causes of death in these patients with those in 16,151 matched controls.
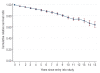
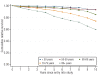
Results: One-, 5-, 10-, and 15-year relative survival ratios were 0.98 (95% CI 0.97-0.99), 0.93 (0.91-0.95), 0.82 (0.79-0.84), and 0.70 (0.64-0.76), respectively. Younger age at diagnosis of the gammopathy was associated with a significantly lower excess mortality compared to that in older patients (p<0.001). The excess mortality among patients with gammopathy increased with longer follow-up (p<0.0001). IgM (versus IgG/A) gammopathy was associated with a superior survival (p=0.038). Patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance had an increased risk of dying from multiple myeloma (hazards ratio (HR)=553; 95% CI 77-3946), Waldenström's macroglobulinemia (HR=infinity), other lymphoproliferative malignancies (6.5; 2.8-15.1), other hematologic malignancies (22.9; 8.9-58.7), amyloidosis (HR=infinity), bacterial infections (3.4; 1.7-6.7), ischemic heart disease (1.3; 1.1-1.4), other heart disorders (1.5; 1.2-1.8), other hematologic conditions (6.9; 2.7-18), liver (2.1; 1.1-4.2), and renal diseases (3.2; 2.0-4.9).
Conclusions: Our finding of decreased life expectancy in patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, which was most pronounced in the elderly and explained by both malignant transformation and non-malignant causes, is of importance in the understanding and clinical management of this disease. The underlying mechanisms may be causally related to the gammopathy, but may also be explained by underlying disease that led to the detection of the hematologic disease. Our results are of importance since they give a true estimation of survival in patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance diagnosed in clinical practice.
Figures
Comment in
-
The significance of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance.Haematologica. 2009 Dec;94(12):1641-4. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2009.013961. Haematologica. 2009. PMID: 19996115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kyle RA, Therneau TM, Rajkumar SV, Larson DR, Plevak MF, Offord JR, et al. Prevalence of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:1362–9. - PubMed
-
- Criteria for the classification of monoclonal gammopathies, multiple myeloma and related disorders: a report of the International Myeloma Working Group. Br J Haematol. 2003;121:749–57. [No authors listed] - PubMed
-
- Kyle RA. Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Natural history in 241 cases. Am J Med. 1978;64:814–26. - PubMed
-
- Kyle RA, Therneau TM, Rajkumar SV, Offord JR, Larson DR, Plevak MF, et al. A long-term study of prognosis in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. N Engl J Med. 2002;346:564–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources