Bicarbonate supplementation slows progression of CKD and improves nutritional status
- PMID: 19608703
- PMCID: PMC2736774
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008111205
Bicarbonate supplementation slows progression of CKD and improves nutritional status
Abstract
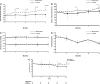
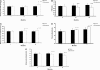
Bicarbonate supplementation preserves renal function in experimental chronic kidney disease (CKD), but whether the same benefit occurs in humans is unknown. Here, we randomly assigned 134 adult patients with CKD (creatinine clearance [CrCl] 15 to 30 ml/min per 1.73 m(2)) and serum bicarbonate 16 to 20 mmol/L to either supplementation with oral sodium bicarbonate or standard care for 2 yr. The primary end points were rate of CrCl decline, the proportion of patients with rapid decline of CrCl (>3 ml/min per 1.73 m(2)/yr), and ESRD (CrCl <10 ml/min). Secondary end points were dietary protein intake, normalized protein nitrogen appearance, serum albumin, and mid-arm muscle circumference. Compared with the control group, decline in CrCl was slower with bicarbonate supplementation (5.93 versus 1.88 ml/min 1.73 m(2); P < 0.0001). Patients supplemented with bicarbonate were significantly less likely to experience rapid progression (9 versus 45%; relative risk 0.15; 95% confidence interval 0.06 to 0.40; P < 0.0001). Similarly, fewer patients supplemented with bicarbonate developed ESRD (6.5 versus 33%; relative risk 0.13; 95% confidence interval 0.04 to 0.40; P < 0.001). Nutritional parameters improved significantly with bicarbonate supplementation, which was well tolerated. This study demonstrates that bicarbonate supplementation slows the rate of progression of renal failure to ESRD and improves nutritional status among patients with CKD.
Figures


Comment in
-
Metabolic acidosis and progression of chronic kidney disease.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Sep;20(9):1869-70. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009070710. Epub 2009 Aug 20. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19696222 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jeffrey A, Kurtz I:Metabolic acidosis of CKD: Diagnosis, clinical characteristics, and treatment. Am J Kidney Dis 45: 978–993, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Mitch WE:Influence of metabolic acidosis on nutrition. Am J Kidney Dis 29: 16–18, 1997 - PubMed
-
- Verove C, Maisonneuve N, El Azouzi A, Boldron A, Azar R:Effect of the correction of metabolic acidosis on nutritional status in elderly patients with chronic renal failure. J Ren Nutr 12: 224–228, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Mitch WE, Du J, Bailey JL, Price SR:Mechanisms causing muscle proteolysis in uraemia: The influence on insulin and cytokines. Miner Electrolyte Metab 25: 216–219, 1999 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

