Reduction of Stat3 activity attenuates HIV-induced kidney injury
- PMID: 19608706
- PMCID: PMC2754106
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008080879
Reduction of Stat3 activity attenuates HIV-induced kidney injury
Abstract
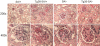
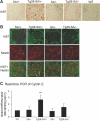
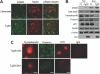
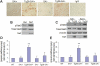
HIV-1 Nef induces podocyte proliferation and dedifferentiation by activating the Stat3 and MAPK1,2 pathways. Activation of Stat3 also occurs in human kidneys affected by HIV-associated nephropathy (HIVAN), but its contribution to the development of HIVAN is unknown. Here, we generated HIV-1 transgenic mice (Tg26) with either 75% Stat3 activity (Tg26-SA/+) or 25% Stat3 activity (Tg26-SA/-). The kidneys of Tg26-SA/+ mice, but not Tg26-SA/- mice, showed increased Stat3 phosphorylation. The Tg26-SA/+ phenotype was not different from Tg26 mice, but Tg26-SA/- mice developed significantly less proteinuria, glomerulosclerosis, and tubulointerstitial injury. Tg26-SA/+ mice exhibited reduced expression of podocyte differentiation markers and increased expression of VEGF and proliferation markers as compared to Tg26-SA/- mice. Primary podocytes isolated from Tg26-SA/+ mice showed increased Stat3 phosphorylation and reduced expression of podocyte differentiation markers. The tubulointerstitial compartment and isolated tubules of Tg26-SA/+ mice also had increased Stat3 phosphorylation and expression of Stat3 target genes. We confirmed that the expression of the HIV-1 transgene and reduction of Stat3 activity did not affect T and B cell development. In conclusion, Stat3 plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of HIVAN.
Figures



Comment in
-
Insight versus Quagmire with compound HIV transgenics.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009 Oct;20(10):2085-6. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2009080811. Epub 2009 Sep 3. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009. PMID: 19729433 No abstract available.
References
-
- United States Renal Data System: 2005 Annual Data Report: Atlas of End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States, Minneapolis, MN, USRDS Coordinating Center, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Wyatt CM, Klotman PE: HIV-1 and HIV-associated nephropathy 25 years later. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2[Suppl 1]: S20–S24, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Wyatt CM, Klotman PE: HIV-associated nephropathy: A case study in race and genetics. Am J Kidney Dis 47: 1084–1085, 2006 - PubMed
-
- D'Agati V, Appel GB: HIV infection and the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 8: 138–152, 1997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

